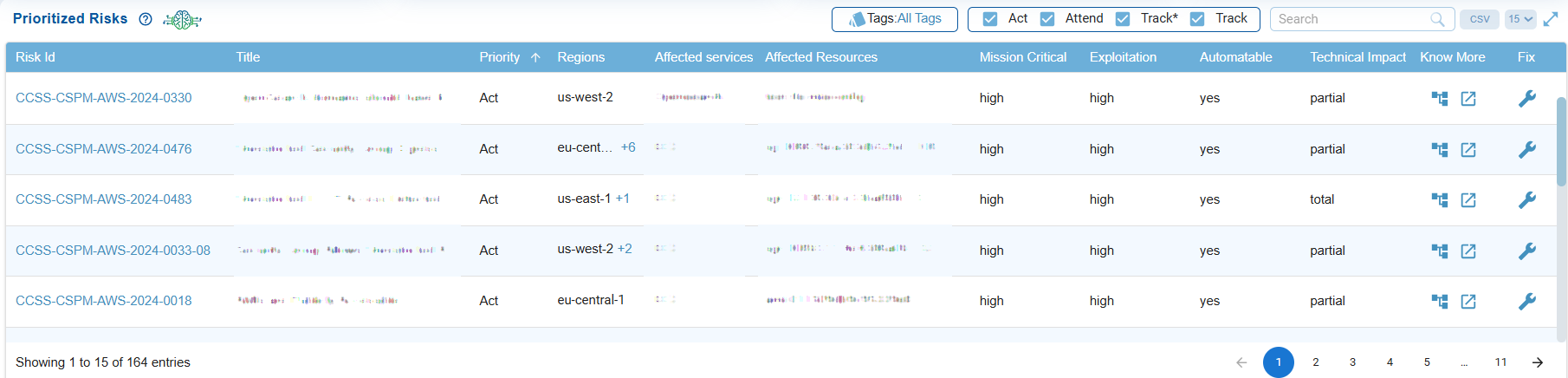
The Prioritized Risks view provides a centralized and prioritized list of security risks, including key attributes such as priority level, exploitability, and technical impact. It assists security teams in quickly identifying which risks require immediate action (Act), need closer monitoring (Attend), should be tracked on an ongoing basis (Track), or remediating misconfigurations within standard update timelines (Track*). This ensures that remediation efforts are focused on the most critical threats.
Each column helps with risk prioritization and remediation planning as described:
Identify Risks by ID and Title
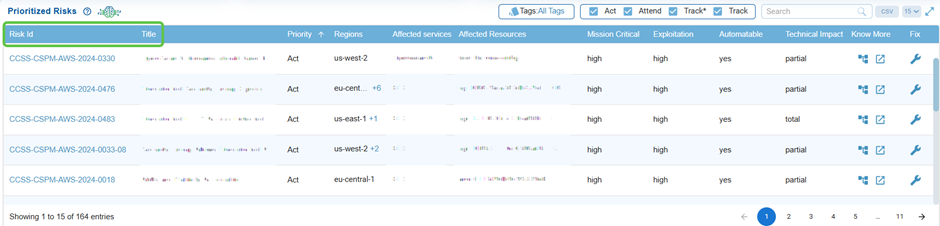
Every risk is assigned a unique Risk ID and a descriptive title, allowing teams to easily identify and reference specific issues, such as weak password policies or IAM misconfigurations.
Click on the Risk Id link to view the detailed breakdown of a specific cloud risk finding.
Review Affected Services and Resources
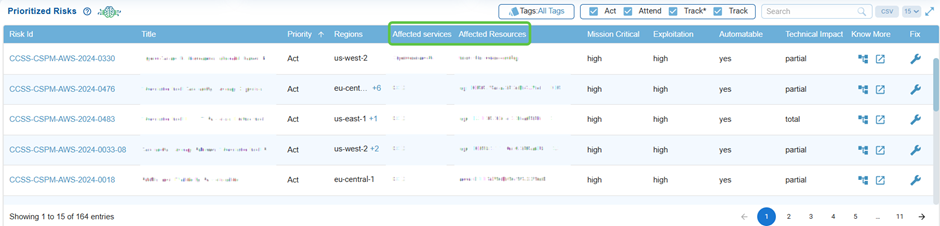
These columns indicate the cloud services and resources affected by the risk, helping teams to evaluate the scope and prioritize critical assets more effectively.
Know the Priority for Action
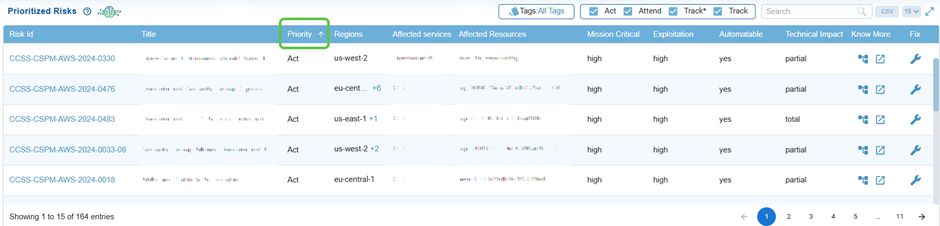
Risks are categorized as Act, Attend, Track*, or Track, which helps prioritize urgency in remediation, making sure that high-severity risks are addressed first.
Evaluate Mission Critical Risks
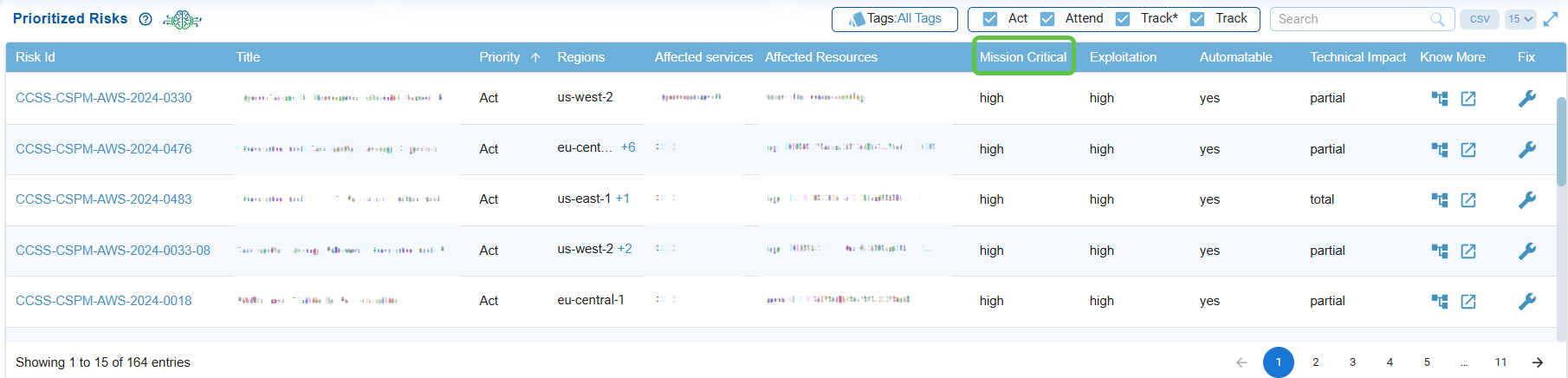
The status(low, medium, or high) indicates if the risk impacts mission-critical systems, helping security teams understand the potential business impact of each finding.
Assess Exploitation Likelihood
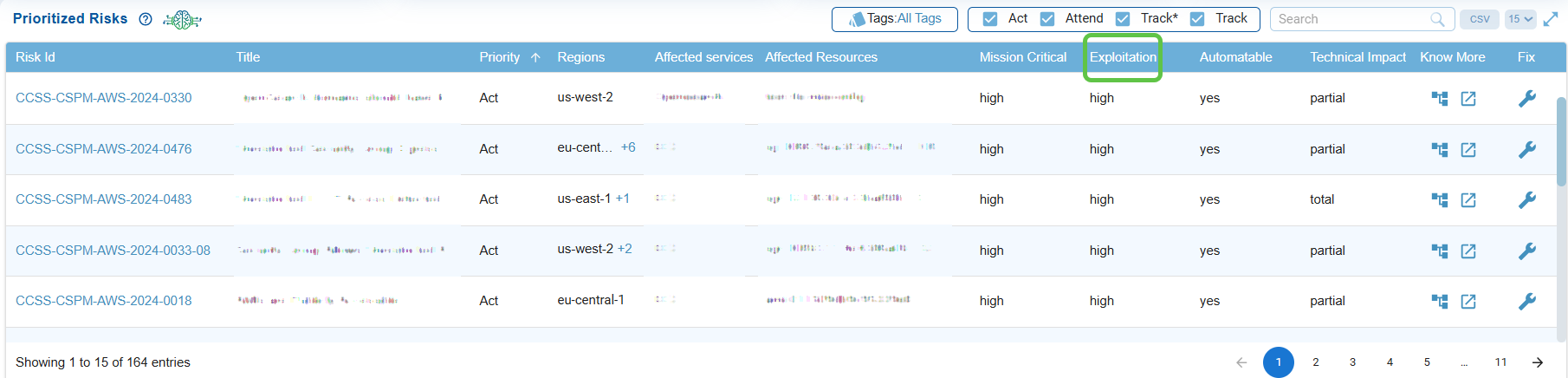
Determines the ease with at which a risk could be exploited (low, medium, or high), supporting decisions on which misconfigurations demand faster remediation.
Check Automation Feasibility
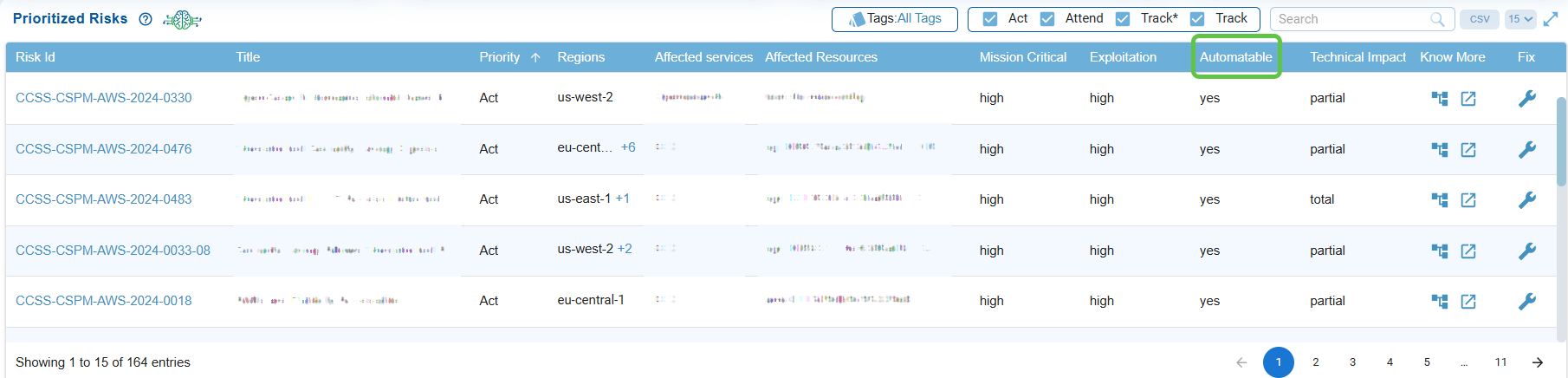
Indicates if the risk can be exploited through automated methods, emphasizing higher urgency if automation is possible.
Click here to read more…
Analyze Technical Impact
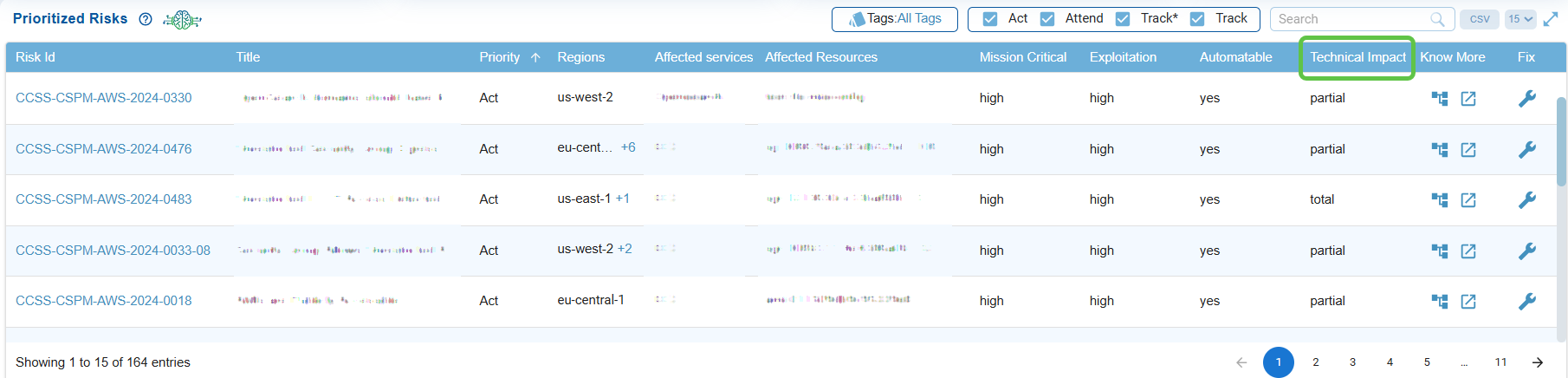
Indicates if the risk can be exploited through automated methods, emphasizing higher urgency if automation is possible.
Click here to read more…
Explore Details from the Decision Tree and Further Examination
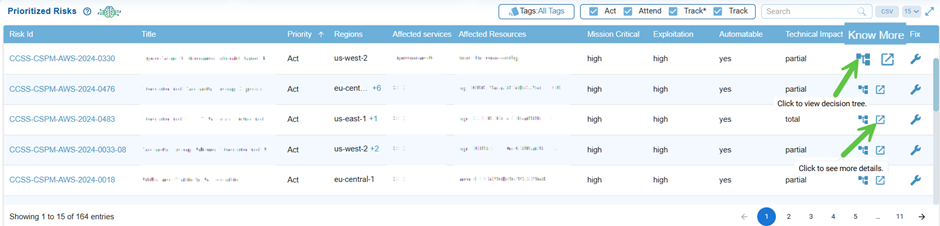
From the Prioritized Risks tabular view in the dashboard, explore details from the Know More column. Under the Know More column, observe the 2 icons: Decision Tree and Further Examination.
Decision Tree
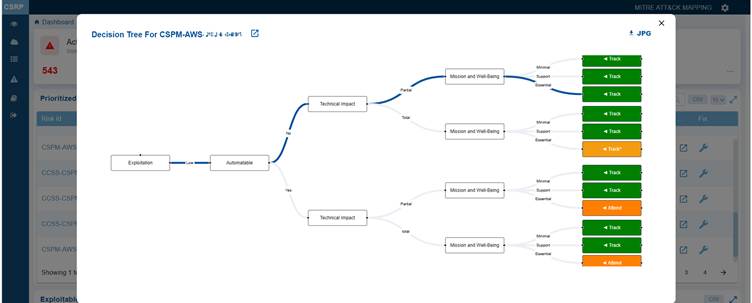
Clicking the Decision tree icon corresponding to a risk opens a logical visualization indicating the origin of the risk or issue, its dependencies, and contributing factors. This visualization is valuable for root-cause analysis and provides a step-by-step breakdown.
The Decision Tree illustrates the factors influencing the decision for risk prioritization, classifying the misconfiguration into one of the following categories: Act, Attend, Track*, and Track.
You also have an option to download and open the tree in JPEG format by clicking the JPG icon on the top right of the pop-up window.
Click the Further Examination button next to the Risk id in the Decision tree window to see more details on the misconfiguration risk.
Further Examination to Mitigate Misconfiguration Risk
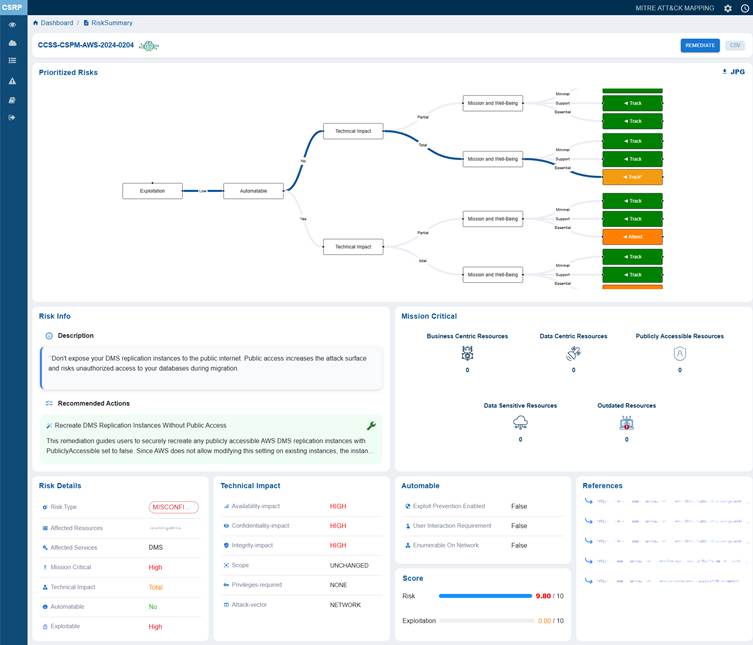
Clicking the More Details button for further examination icon under the Know More column in Prioritized Risks view opens up the Risk Summary view from which you can examine the following:
Trace Exploitation Path to Business Impact from Prioritized Risk Summary Visualization
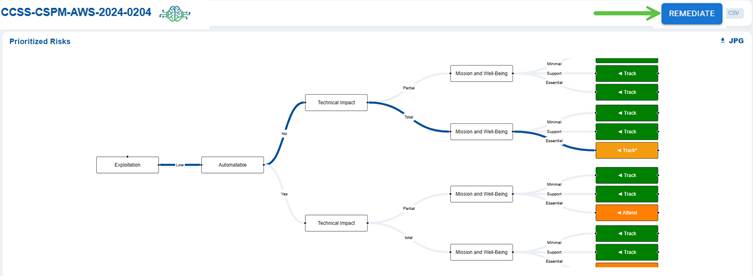
This section visualizes the potential exploitation flow of the misconfiguration risk. It shows how an exploitation event can lead to a technical impact and further escalate to affect mission and well-being. Each branch of the flow ends with viewable tags such as Track or Attend, guiding security teams on what actions to prioritize for monitoring and remediation.
Note: The REMEDIATE button located in the top-right corner above the Decision Tree, becomes active only when a remediation is available for the associated risk ID or rule.
Understand and Mitigate the Identified Risk from Risk Info
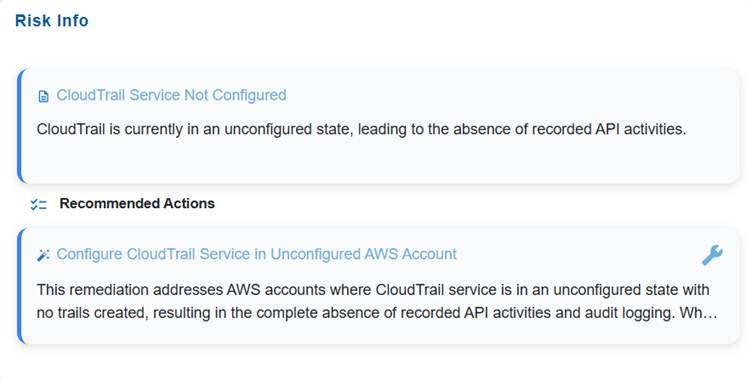
The Risk Info block is intended to give a concise yet complete overview of an identified risk. It captures the title and description to define the nature and context of the issue, and includes recommended actions to guide remediation or mitigation efforts. This ensures stakeholders quickly understand what the risk is and how to address it.
The Recommended Actions block outlines the remediation actions and provides the Fix icon to automatically redirect you to the relevant tool in Saner CSRP for resolution. Click to read more on How to Remediate in Saner Cloud?.
Review Mission Critical Resource Exposure

The mission-critical block displays a diverse range of resources, each with unique risk considerations. It includes a combination of business-centric resources essential for daily operations, meaning any disruption could directly affect productivity and service continuity. Additionally, it encompasses data-centric resources that manage significant information processing and storage.
This block also contains publicly accessible resources, which increase exposure to external interactions, as well as data-sensitive resources that require enhanced Review and Prioritization due to confidentiality risks. Furthermore, outdated resources may present reliability or security concerns if they are not updated.
For example, the mission critical block showing 2 business-centric resources, 4 data-centric resources, 4 publicly accessible resources, 1 data-sensitive resource, and 1 outdated resource, represents a balanced mix of operational, data, and public-facing components.
Review Core Risk Attributes from Risk Details
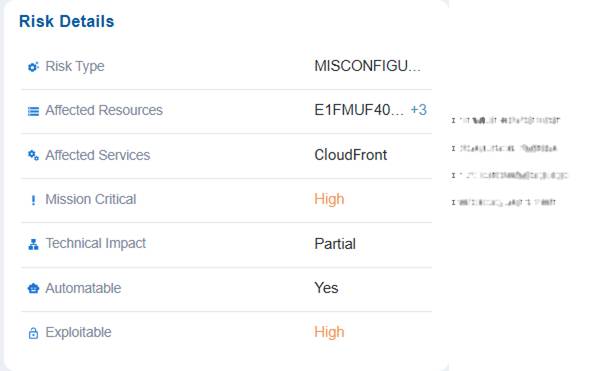
The Risk Details block offers a structured overview of identified risks by outlining their type, the affected resources and services, and if they are mission-critical. It also emphasizes the technical impact of each risk, along with indicators representing if the risk can be automated or is easily exploitable.
This organized breakdown assists in prioritizing remediation efforts, understanding exposure levels, and aligning mitigation strategies with business impact.
Note that you have an option to view and choose the appropriate resource by clicking the + symbol in the Affected Resources value.
For example, a misconfiguration risk has been identified in resource X within the CloudFront service carries high mission criticality, meaning it could significantly affect core operations if exploited. The technical impact is partial, so while not a complete failure, it could still disrupt functions or expose vulnerabilities. The risk is marked as highly exploitable, making it an attractive target for attackers. Since it is automatable, remediation can be streamlined through automated fixes or security tools, reducing response time compared to manual intervention.
Assess Technical Impact of Misconfiguration
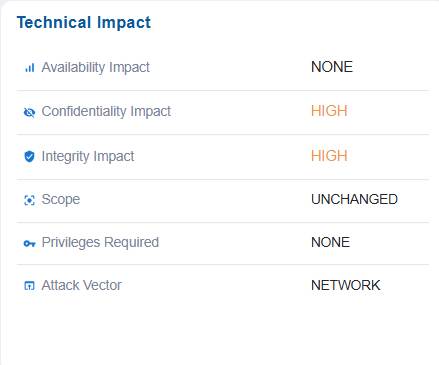
The Technical Impact block presents a structured assessment of how a misconfiguration or risk affects system operations. It details the impact on availability, confidentiality, and integrity, specifies which components are affected, identifies any required privileges needed to exploit the issue, and describes the attack vector through which the risk can be realized. This information enables stakeholders to understand the severity and nature of the technical consequences, prioritize mitigation efforts, and align security controls with the potential business impact.
For example, issue has no impact on system availability(NONE) indicates services continue running normally. However, it poses a high risk to confidentiality and integrity, meaning sensitive data could be exposed or altered. The scope is unchanged, indicating the misconfiguration affects only the current resource and does not extend to other components. No privileges are required to exploit it, making it easier for an attacker to target, and the attack vector is network-based, meaning it can be exploited remotely over the network.
Determine Exploitability Automation Potential
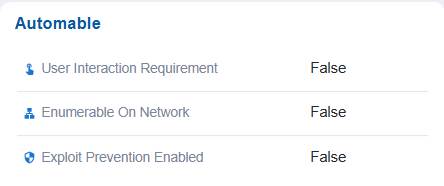
In this case, the Automatable section assesses if the exploit can be automated. In this case, the dashboard indicates that exploit prevention, user interaction requirement, and network enumeration are all set to false, suggesting exploitation would not require additional interaction but also cannot be automatically prevented using existing security controls.
Note: If set to True, the “Exploit Prevention Enabled” option indicates that protective mechanisms are in place to block exploitation, making the system more secure. When “User Interaction Requirement” is set to True, it means that user action is necessary for exploitation to occur, which reduces the likelihood of automated attacks. On the other hand, if “Enumerable on Network” is True, the vulnerability becomes discoverable over the network, increasing the risk of large-scale automated exploitation.
Measure Risk Severity and Exploitation Likelihood
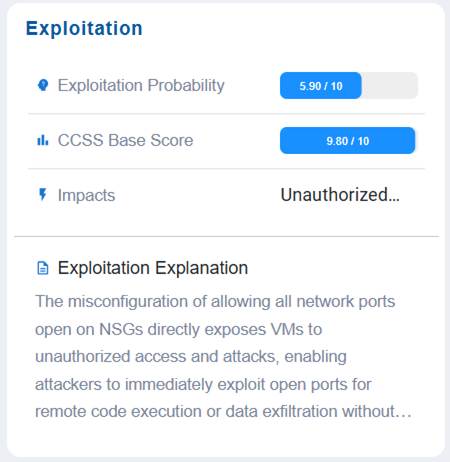
The Exploitation block helps assess and communicate the likelihood and severity of a risk being exploited. It captures the exploitation probability, the CCSS base score as a standardized severity rating, the potential impacts of a successful exploit, and a clear exploitation explanation to describe how and why the risk could be leveraged by an attacker.
This structured view helps stakeholders gauge both the feasibility and consequences of exploitation, supporting informed prioritization and remediation planning.
In this example, the Exploitation block values indicate that the issue has a moderate likelihood of exploitation (5.90/10), but carries an extremely high severity score (CCSS 9.80/10), meaning the potential consequences are critical. If successfully exploited, it could lead to unauthorized access or actions, posing a major security concern. The exploitation explanation provides context on how the weakness might be leveraged, emphasizing the need for prioritized remediation despite its moderate probability, since the impact would be highly damaging.
Utilize Reference Material to Support Secure Remediation

In this case, the References section provides direct links to relevant documentation to support remediation.
In this example, references are provided for cloudtrain concepts and so on. Click on the link(as shown in the screenshot) to open the relevant documentation.
Related Topics


