Overview
Automation and Job-driven Patch Remediation is a risk-aware approach to secure cloud environments by identifying, prioritizing, and resolving security findings.
The strategy begins with prioritizing remediation based on risk assessment(whether a resource is actively being exploited, how important the affected system is to business operations or data security etc.), confidence levels, and the age of anomalies, making sure that the most impactful and potentially exploitable anomalies are addressed first.
To streamline the process of remediation, organizations adopt standard remediation strategies, from job-based patching initiated through platforms like CSPM (Cloud Security Posture Management), CIEM (Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management), and CSPA (Cloud Security Posture Anomaly), to automated remediation configured to run on predefined schedules. These capabilities support users to initiate bulk remediation, remediate identity-specific findings, and even directly launch relevant tools for remediation from a central tool like CSRM (Cloud Security Remediation Management).
Ultimately, this approach fulfils the goal of reduced response time, lower risk exposure, and improved cloud compliance through job-driven and automated patch-driven remediation.
Strategies to Prioritize Remediation
Effective remediation goes beyond merely identifying issues. It requires meticulous prioritization. Instead of treating all findings equally, a risk-based prioritization strategy must be adopted focusing efforts on issues that pose the greatest threat. This calls for considering factors such as exploitability, asset criticality, and exposure.
By understanding confidence levels, teams can distinguish between high-assurance findings, allowing them to concentrate on verified risks.
Additionally, considering patch aging helps identify older or previously overlooked anomalies that may pose increasing exposure over time.
Together, these strategies facilitate security teams to systematically prioritize and address the most critical and high-risk issues first, resulting in improved efficiency and overall security posture.
Understanding Confidence Levels to Prioritize Remediation
Addressing detected anomalies requires following specific remediation steps that are prioritized based on the severity of the risk. The focus is on resolving critical vulnerabilities and misconfigurations that present the greatest threats. To do this, issues are classified as high, medium, or low to help effective allocation of resources during the remediation process.
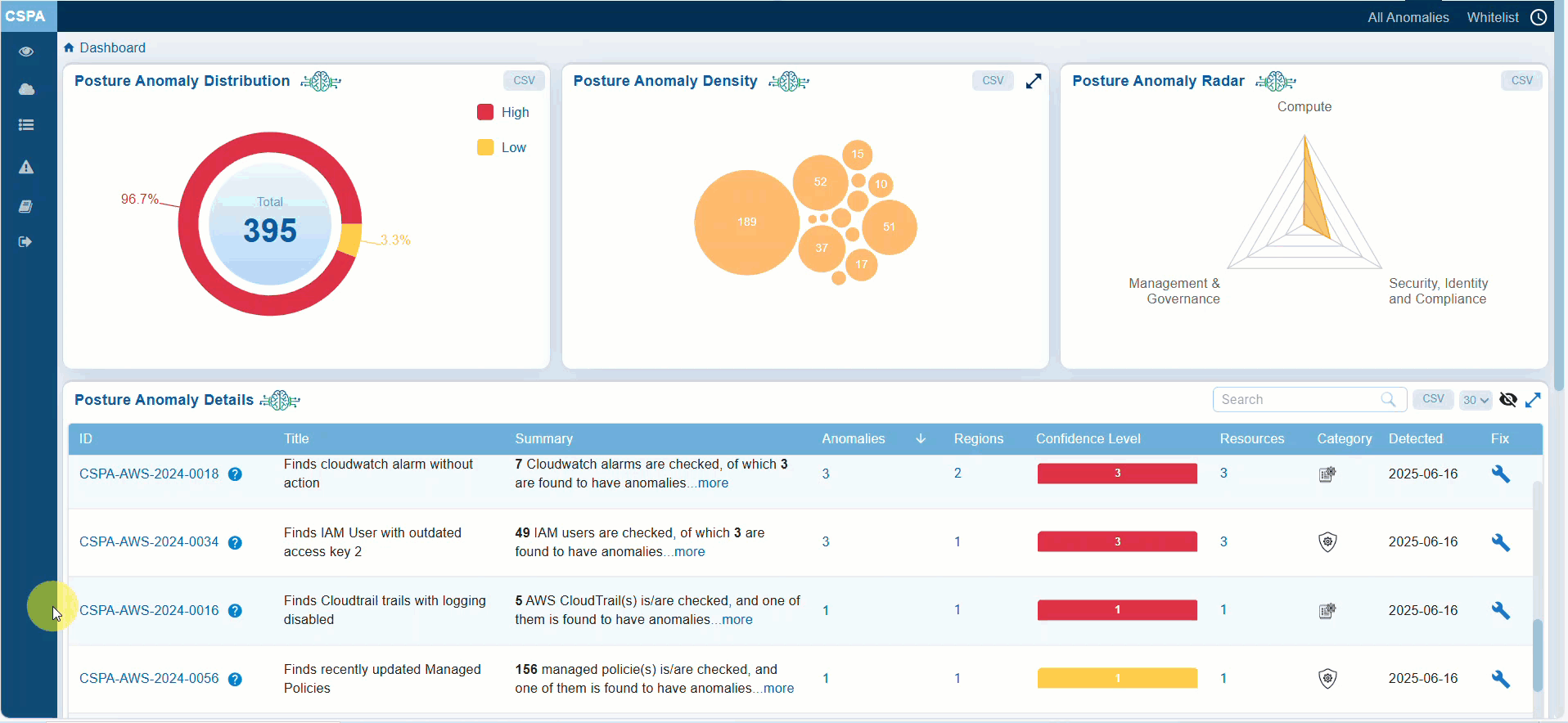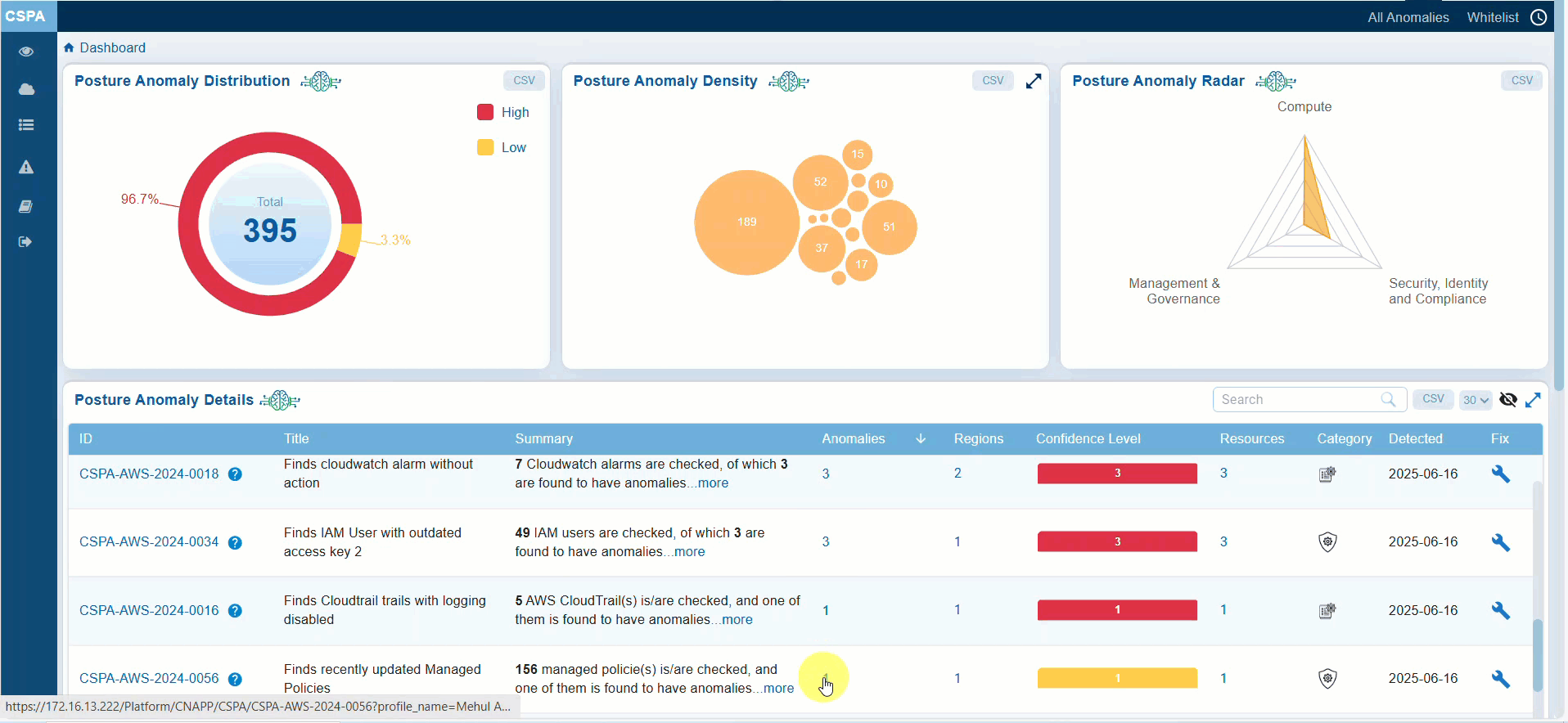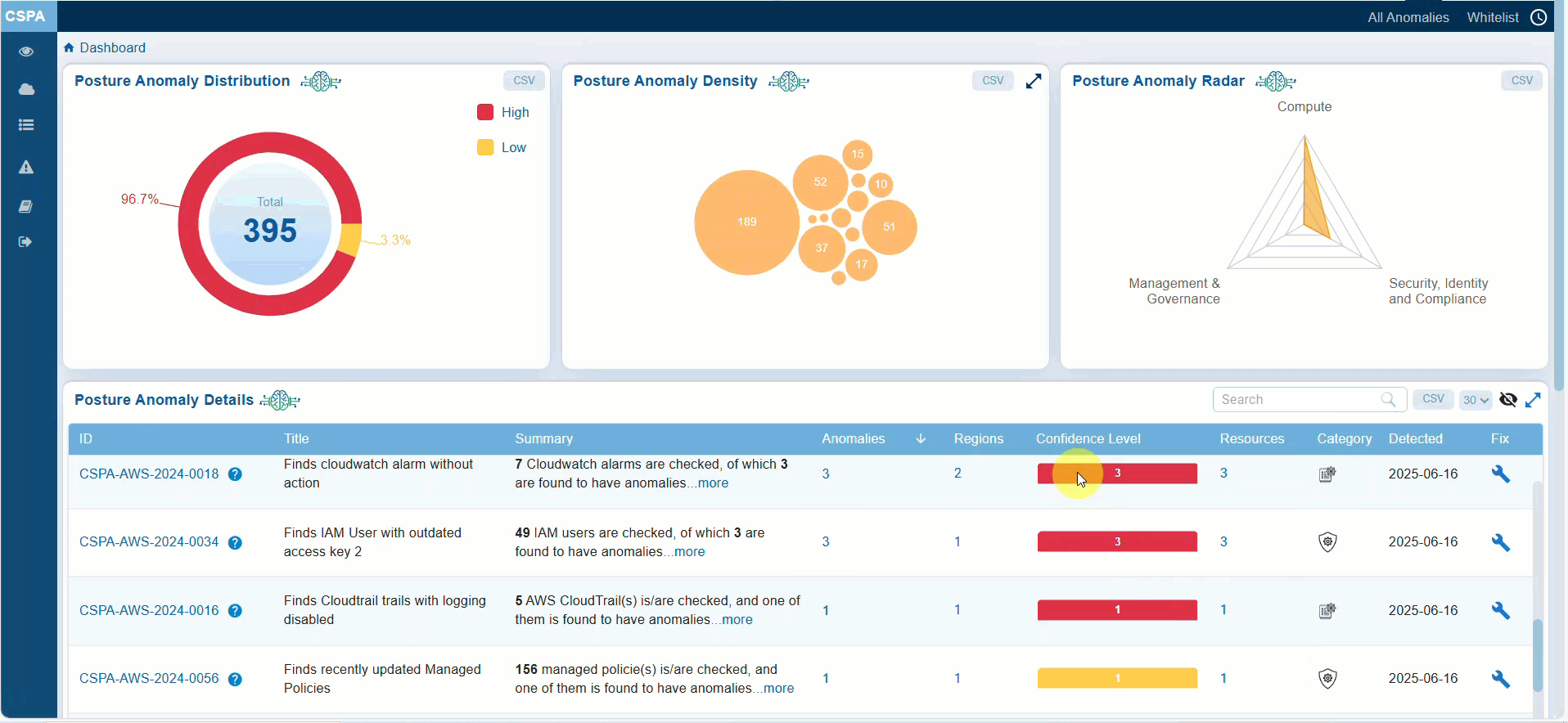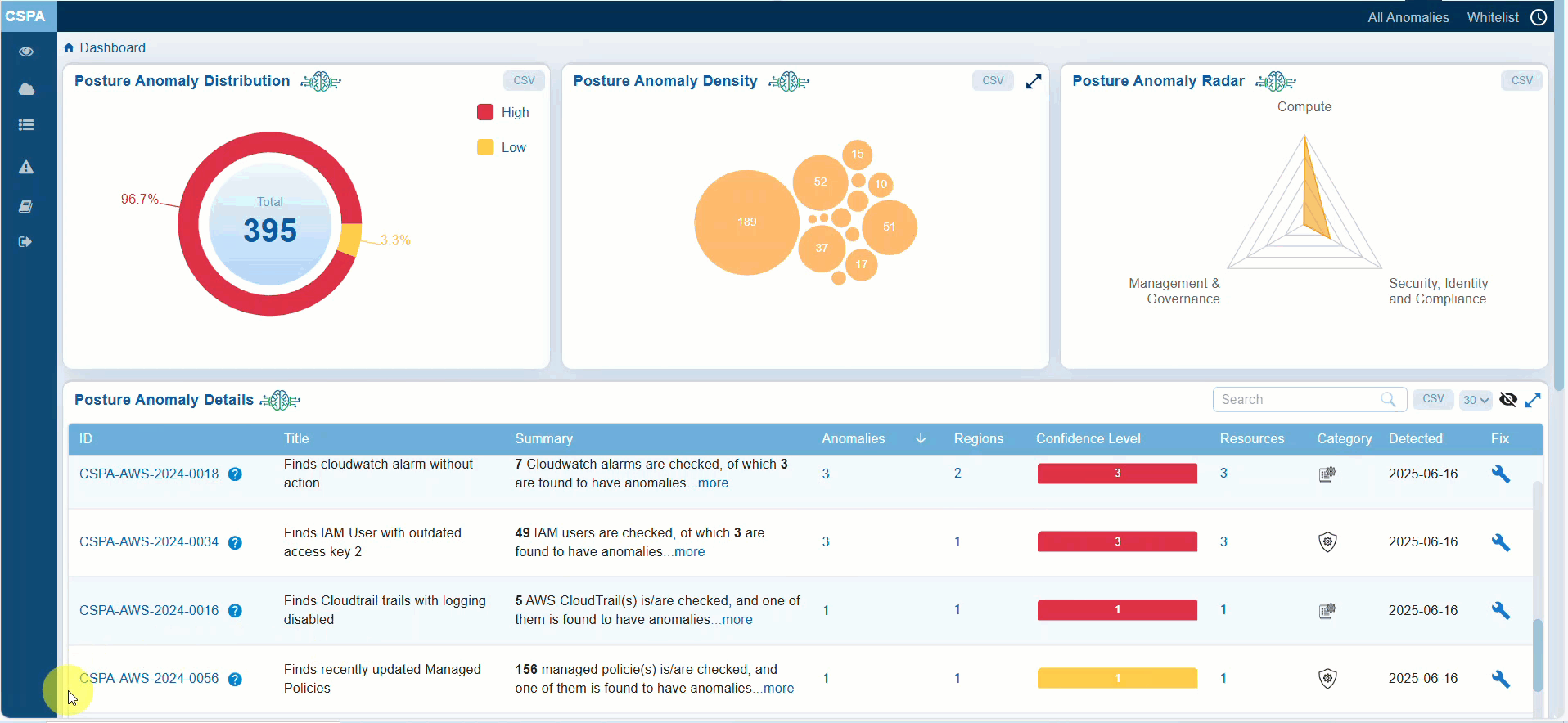
The ”Confidence Level” in CSPA detects deviations and anomalies by observing the collective data within the organization that could increase the attack surface or pose genuine risks.
The classification of anomalies into Red, Orange, and Yellow confidence levels follows a structured statistical approach that is part of a rules-based system. This approach uses statistical thresholds based on mean and standard deviation, providing a clear and effective foundation for identifying behavior that deviates from the norm. It helps in classifying the confidence and severity of anomalies, as well as prioritizing them for investigation or automated response.
This method makes sure that data-driven triage aligns effectively with automated CIEM (Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management), CSPM (Cloud Security Posture Management), or anomaly detection systems. It involves collecting telemetry or behavioural data over a period of time and mapping thresholds to confidence levels. Anomalies are classified based on the magnitude of deviation or as percentile-based outliers.
Users can further view these confidence levels in the dashboard to make informed, risk-based decisions.
A real-time view of confidence levels in CSPA:
Prioritizing and Addressing Older or High-Risk Anomalies with Patch Aging
Patch aging refers to the amount of time that has elapsed since a vulnerability was first detected but has not yet been remediated. As the patch age increases, so does the risk, since known vulnerabilities become easier targets for exploitation due to widespread public knowledge and the availability of exploits.
Unaddressed anomalies with high patch aging not only raise compliance concerns (e.g., CIS, NIST, ISO standards) but also increase the attack surface in production environments.
What do Older Anomalies Indicate?
Older anomalies often point to neglected vulnerabilities that may have been deprioritized due to incorrect risk assessments or difficulties in applying patches because of environmental complexities, such as system dependencies. Furthermore, these longstanding issues increase the potential exposure window, making them appealing targets for attackers if they remain unpatched for an extended period.
Calculating Patch Age
Patch age is an important metric that helps security teams evaluate how long an anomaly or misconfiguration has gone unresolved. To effectively calculate and respond to patch age, key indicators are utilized such as:
- Detection Date provides a clear starting point, indicating when the issue was first identified.
- Risk based Prioritization further enhances this approach by evaluating the severity of the issue in relation to its age and confidence level. Older vulnerabilities that are critical in nature and have high confidence scores are flagged for immediate action, making sure resources are focused on the most dangerous and time-sensitive threats.
- Confidence-level scoring helps prioritize older issues that are not only overdue but also confirmed as high-risk, combining urgency with certainty.
Together, these indicators offer valuable insight into patch aging, aiding in more accurate prioritization and quicker remediation of the most critical and long-standing security issues.
Detection Date as an Indicator for Patch Age
The Detection Date is the timestamp that marks when a misconfiguration or anomaly is first identified in the environment. This date serves as the starting point for calculating patch age, the duration for which an issue has remained unresolved.
Using the Detection Date as an indicator provides essential visibility into how long a security issue has persisted without a resolution. This approach helps security teams in several ways:
- Prioritization: It allows teams to prioritize older vulnerabilities that have been exposed for the longest time and may be at a higher risk of exploitation
- Tracking delays: Teams can track patching delays and measure compliance with both internal Service Level Agreements (SLAs) and external regulatory timelines
- Assessing risk maturity: Aged issues often highlight gaps in vulnerability management processes or resource bottlenecks, which helps in assessing the organization’s risk maturity
For example, if a critical vulnerability was detected 45 days ago and has not yet been patched, the Detection Date underscores the aging issue and raises its priority in remediation workflows.
Detection Date helps organizations gain valuable time-based context. This helps them to move beyond merely static severity scoring and adopt a more dynamic, risk-aware approach to anomaly or misconfiguration management.
Risk-based Prioritization to Address Aged and Critical Anomalies
Risk-based prioritization is a strategy that evaluates multiple factors, such as severity, exploitability, and the age of vulnerabilities, to determine which issues must be addressed first. A key aspect of this approach is to assign higher priority to older anomalies that are classified as critical.
When an anomaly has a high severity rating (for example, due to its potential impact or active exploitation) and not remediated for a long time, it poses a significant risk to the environment. These aged, high-severity issues are flagged for immediate action for several reasons:
- They have been exposed for a longer period, increasing the likelihood of exploitation.
- Their critical nature means that successful exploitation could lead to major data breaches, service disruptions, or compliance violations.
- Attackers often focus on well-known, unpatched misconfiguration publicly available resources.
By prioritizing anomalies based on both risk severity and how long they have been detected, organizations can ensure that the most dangerous and long-standing issues are resolved first. This improves both their security posture and operational efficiency. This approach also avoids the inefficiency of treating all anomalies equally, allowing resources to be directed where they are most needed.
What to Interpret from Patch Aging and Patching Impact Charts?
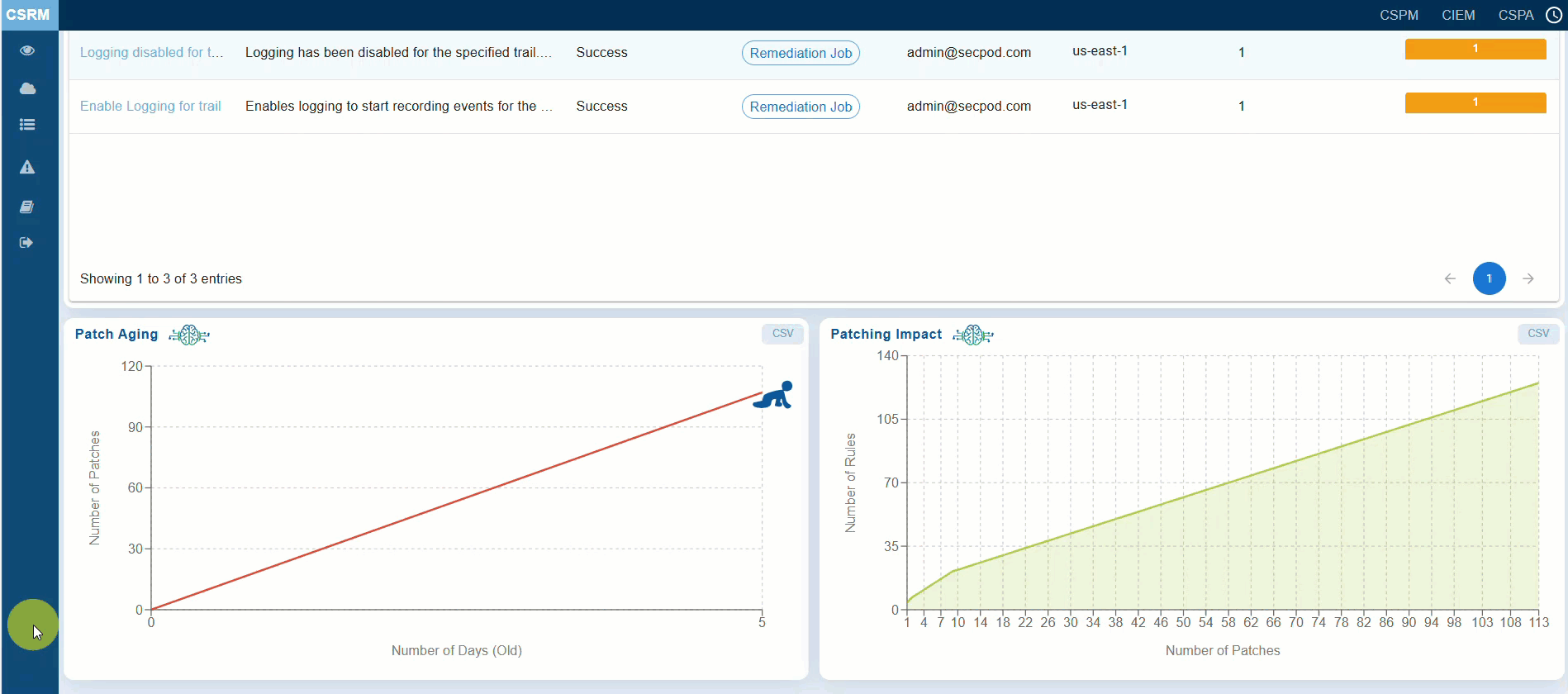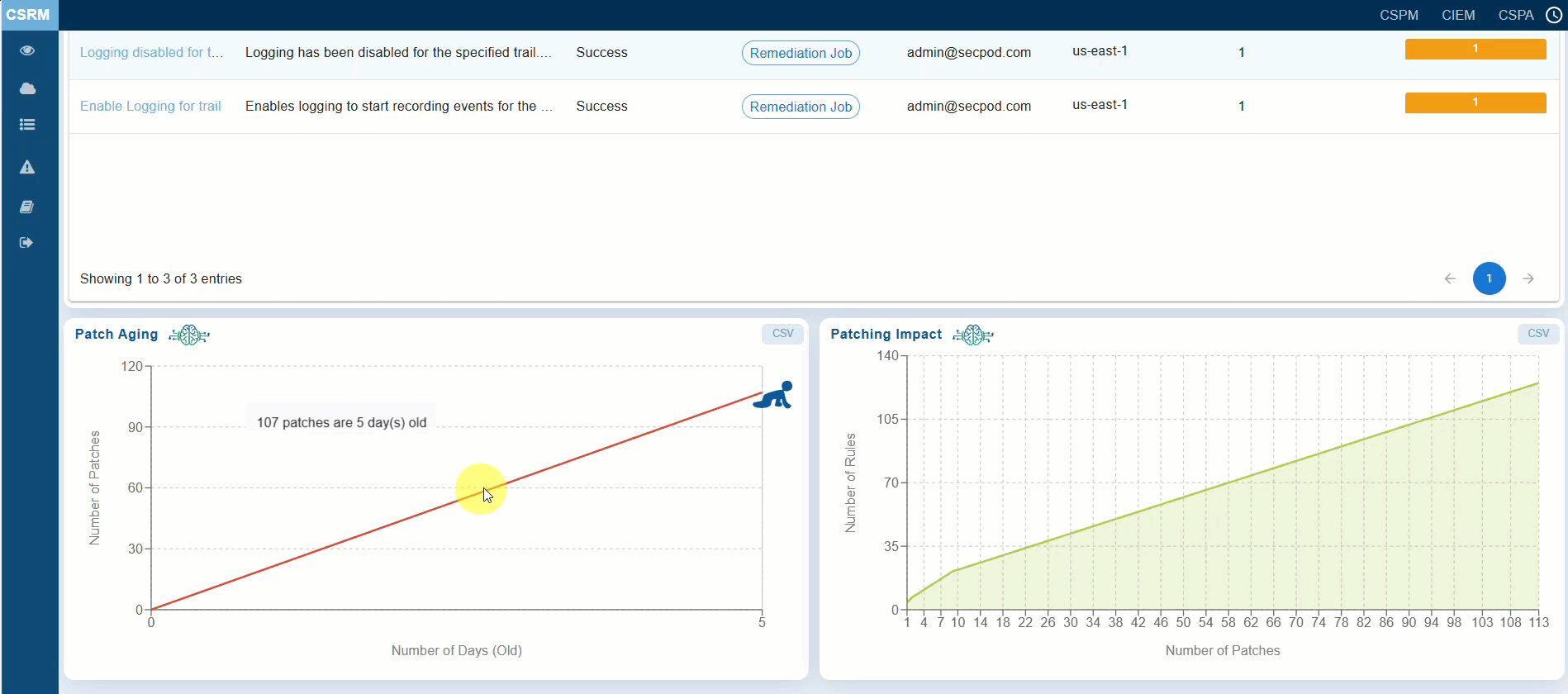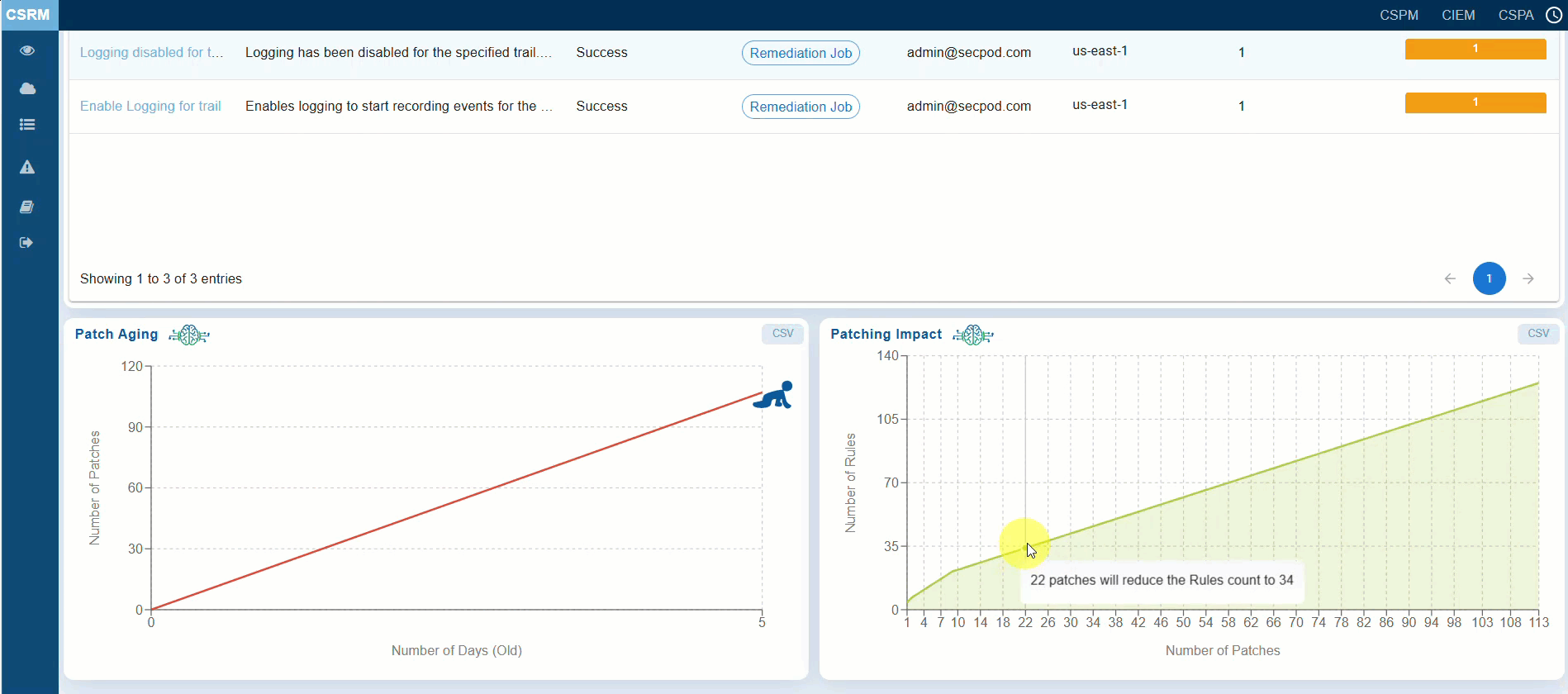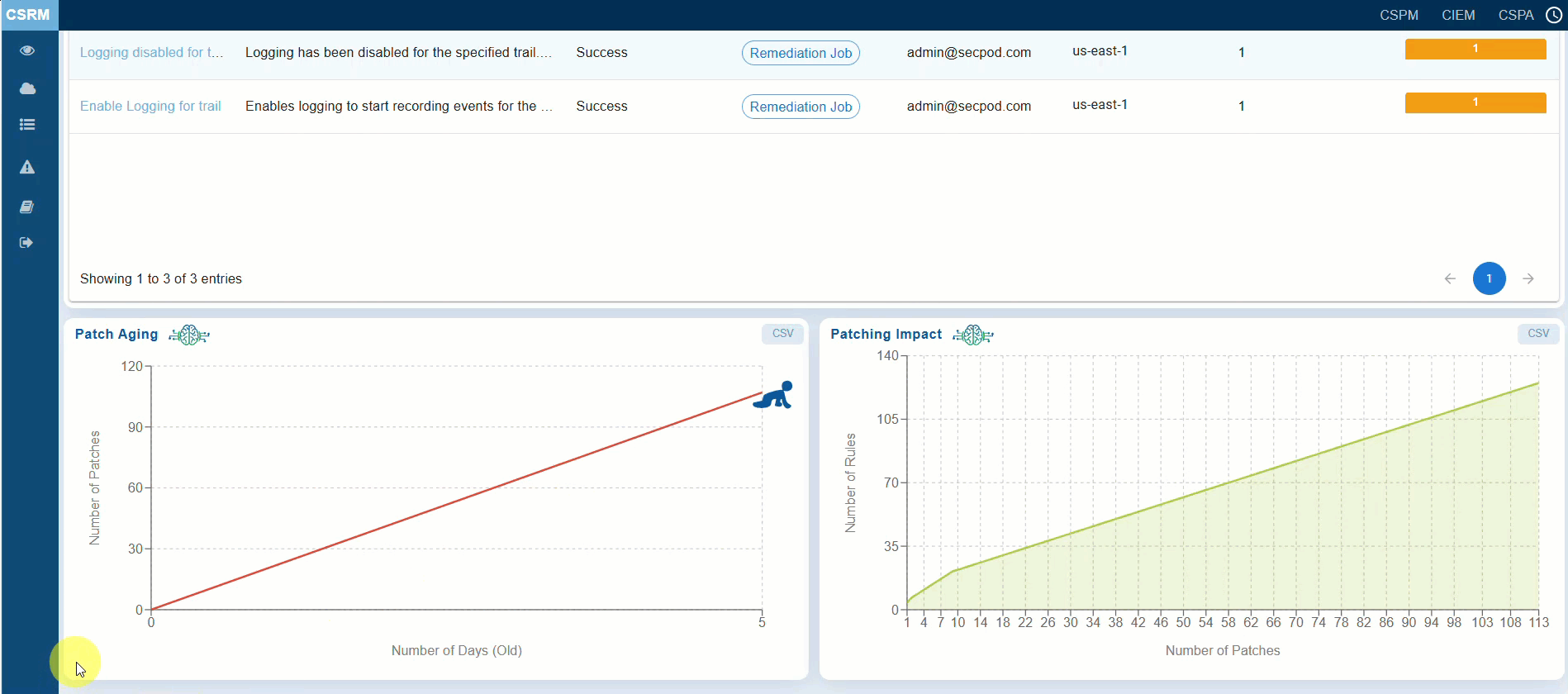
The “Patch Aging” chart visually represents the duration during which patches remain unapplied in a cloud infrastructure. It illustrates the relationship between the number of pending patches and the number of days they have been outstanding. This chart assists organizations in tracking and managing their patch deployment timelines. An upward trend indicates delays in patch deployment, which increases the organization’s exposure to anomalies and misconfigurations over an extended period. The creative visual employs characters or icons along the timeline to depict different stages of patch aging, including growth, decline, and subsequent resurgence.
The “Patching Impact” chart helps you to prioritize patches that have the maximum impact, ensuring critical anomalies and misconfigurations are addressed first. The graph also illustrates the relationship between the number of patches applied and the reduction in the number of rules. X-Axis indicates the number of patches applied Y-axis indicates the number of rules affected. The point that you highlight by moving your cursor indicates the impact of patching on reducing anomalies and misconfigurations.
Confidence-level Scoring to Prioritize Patches with Certainty and Urgency
Confidence Scoring measures how certain the system is in confirming that a detected anomaly represents a legitimate security risk. When combined with patch aging it identifies issues that are not only confirmed risks but also urgently need remediation.
For instance, a high-confidence (Red) anomaly indicates that the system has strong evidence of its real and impactful nature. If this anomaly has remained unpatched for a long time, it becomes even more critical to address, as it poses both a certain threat and an extended exposure window.
This combination of patch aging with confidence levels help security teams to:
1. Focus only on anomalies with high certainty.
2. Speed up responses to aged, high-confidence issues that present the greatest risk.
3. Optimize resource allocation by targeting anomalies that matter most, those that are both validated and longstanding.
In summary, confidence scoring with patch aging sharpens remediation decisions, ensuring that urgent, real threats are quickly addressed, while lower-confidence or newer issues can be managed with less urgency.
Related Topics


