Product Overview
Saner Network Scanner helps you identify vulnerabilities and misconfigurations across all IP-enabled devices in your Organization. And to do this – you don’t have to invest in additional hardware.
Network Scanner scans your network by leveraging the endpoints that exist in your network. Saner Network Scanner is built on a hub and spoke model – which effectively reduces the scan time required to scan and discover vulnerabilities in your network – making the entire process seamless and continuous.
Features of Saner Network Scanner
- Network Scanner tool can detect network topology, devices, and operating systems and perform service fingerprinting across all IP-enabled devices.
- Using Network Scanner, you can identify vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in network devices. Additionally, you can perform an external security posture analysis of endpoint devices.
- With Saner Network Scanner, you don’t need to invest in additional hardware to have network scanning capability. Instead, the Network Scanner tool automatically identifies endpoints and designates them as network scanners.
- You can automate daily scans using Network Scanner to perform periodic scans on your network.
- Saner Network Scanner supports authenticated network scans. You can provide credentials to the network scripts and perform a scan on network devices in your infrastructure to identify the vulnerabilities existing on these devices.
- Saner Network Scanner supports agentless scan – you don’t have to deploy Saner Agent on target devices and still perform vulnerability and compliance scans.
Saner Network Scanner Pre-requisites
Endpoints running the below-mentioned OSs can be designated as Network Scanners.
- Windows (32bit and 64-bit)
- macOS
- Linux (only 64-bit is supported)
Endpoints running Linux OS (32-bit), Alpine Linux (32-bit and 64-bit) and AIX (32-bit and 64-bit) can’t be designated as network scanners.
Also, you must have an active subscription to either one of the tools – Vulnerability Management, Compliance Management, or Asset Exposure- to use the Network Scanner feature.
Designate an Endpoint as a Network Scanner
You need to designate endpoints within your network as network scanners. You can do this in two ways
- Using the Wizard available in the Saner tool to designate an endpoint as a network scanner automatically.
- Designating endpoints as network scanners from the list of Saner recommended devices.
Designate a Saner Agent as a Network Scanner using the wizard
In this method, we use the Saner Agent installed on an endpoint device and designate it as a Network Scanner.
Follow the below steps to designate an endpoint as a Network Scanner using the wizard.
1: Log in to the Saner web console. Click the Control Panel icon ![]() located at the top right corner of the page.
located at the top right corner of the page.
2. On the Control Panel page, from the organization drop-down menu, select the organization you want to work with.
3. Select CVEM from the product drop-down menu.
4. Under the Scanners menu, click Network Scanner.
5: On the Designate and Manage Network Scanners page, click the Create New Scanner button.
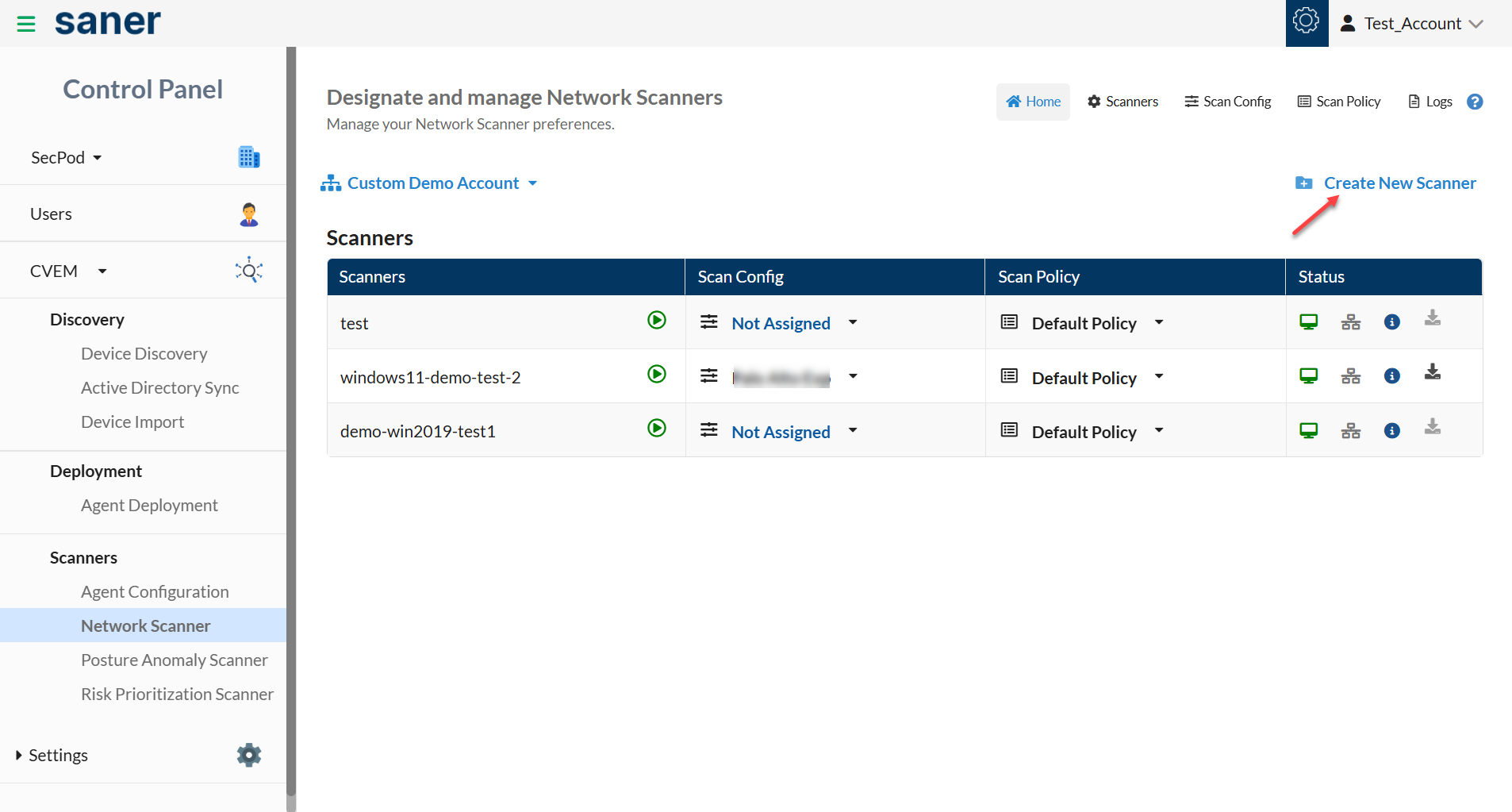
A pop-up screen with a drop-down menu appears. You will see two options here listed under Scanner Type.
- Designate an existing agent to Network Scanner.
- Setup and designate a new agent to Network Scanner.
4: Select the option – Designate an existing agent to Network Scanner.
A drop-down box with all the Saner Agents available in the Account that can be designated as a Network Scanner appears.
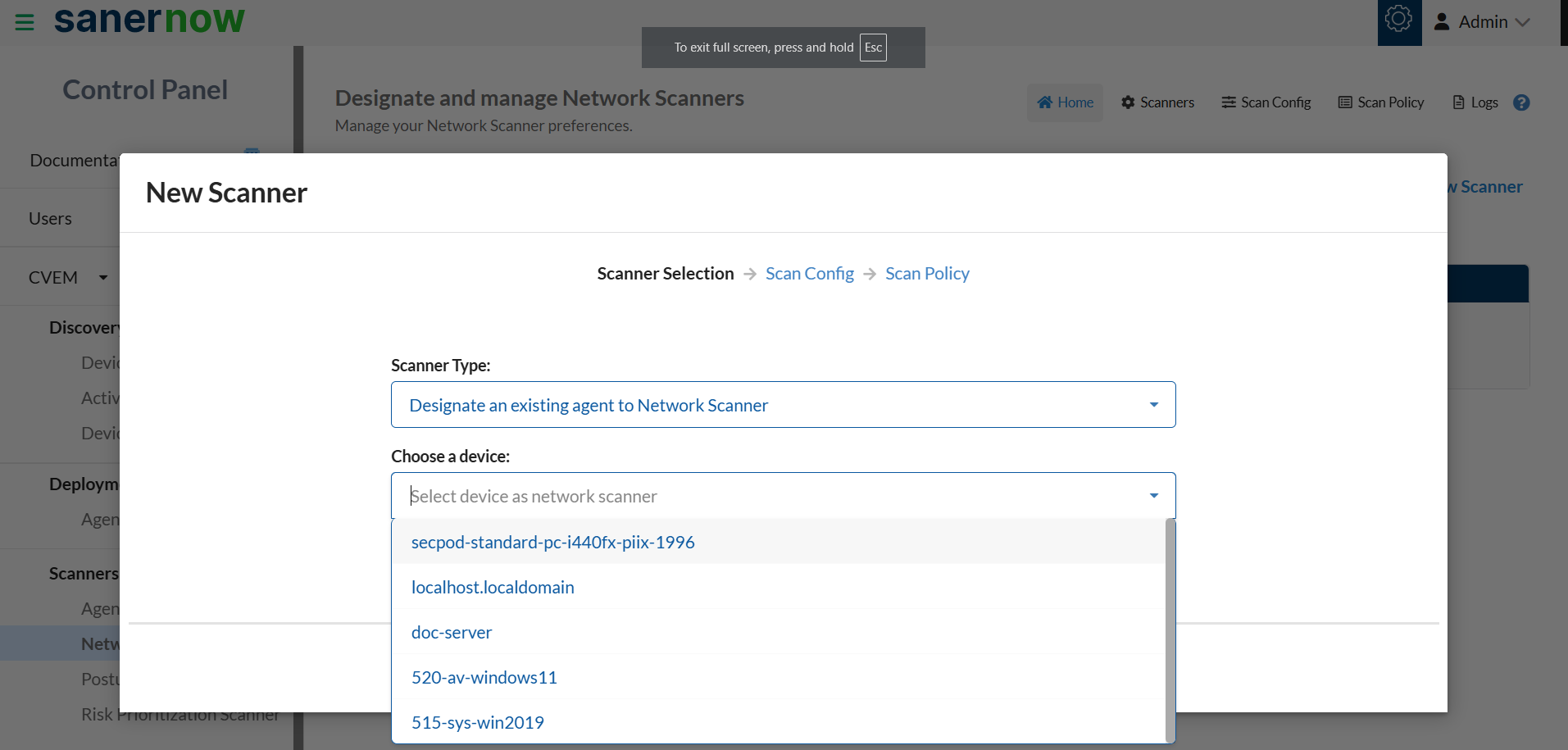
5: Select the device you want to be designated as a Network Scanner and click the Next button.
The Scan Config screen appears.
6: You must fill in the information in the text boxes marked with an asterisk (*). Let’s look at each of these textboxes present on the screen and the type of information you need to provide.
Name: – You must specify a name for the Scan Config
Targets – Mention the IP addresses of the targets you wish to scan. The IP addresses must be specified in a comma-separated list of target IP addresses or domain names for scanning. Target IP addresses can also be specified using CIDR notation. For example, 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.1.1/32 or 192.168.1.1-10.
Exclude List: Mention the IP addresses of the targets that need to be excluded by the network scanner while performing a network scan. You can specify multiple IP addresses separated by a comma that needs to be excluded by the Network Scanner.
Select Ports: This drop-down box provides you with five options. You need to select one of these five options.
- Default Ports
- Top 1000
- Top 500
- Top 100
- None
However, if you want to specify your own set of custom ports, select the checkbox Enter Custom Ports and specify the TCP and UDP ports you want to be scanned by the Network Scanner.
7: Select the Scan Schedule. You can select the scan to run at the below intervals.
- None
- Daily
- Weekly
- Monthly
8: Select the Run Scan schedule. Once you do that, you will see a pop-up screen where you must choose the Scan Policy. By default, the Default Policy gets selected in the drop-down box. Saner configures the Default Policy. Any other Scan Policy that you have configured for the selected account will be shown here in the drop-down list. Click the Create button once you have chosen the Scan Policy.
| Note: You can opt to change the Scan Config and Scan Policy whenever you launch a network scan using Saner Network Scanner. |
Set up a New Saner Agent as a Network Scanner using the wizard
In this method, we install the Saner Agent on an endpoint device and then promote the agent as a Network Scanner.
1: Select the option Setup new agent to perform network scan. And select the Saner Agent Installer depending on the operating system installed on the endpoint.
2: Install Saner Agent on the device. In the meantime, while Saner Agent is getting installed, the wizard will wait for the Saner Agent to get installed and communicate back to the wizard.
3: Saner Agent installed device pops up on the wizard. Select the device and click the Next button.
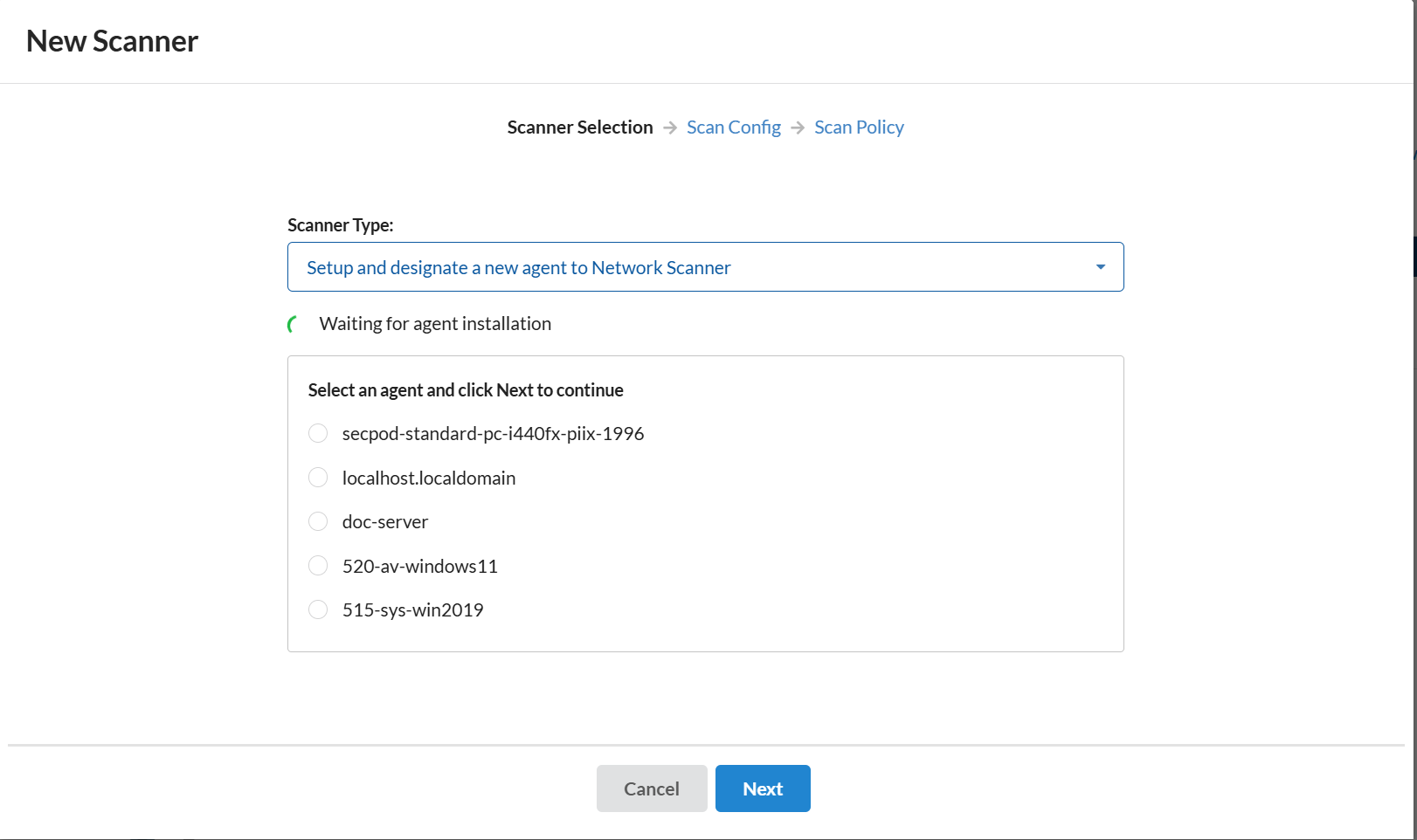
4: Now follow the instructions specified in Steps 7- 10 from the section – Using the Wizard to designate an Agent as a Network Scanner.
Saner Network Scanner is now ready to perform a network scan on your network.
Manually designate endpoints as Network Scanners
1: On the Designate and Manage Network Scanners page, click the Scanners button.
A list of devices from the Account that can be designated as Network Scanners is shown here.
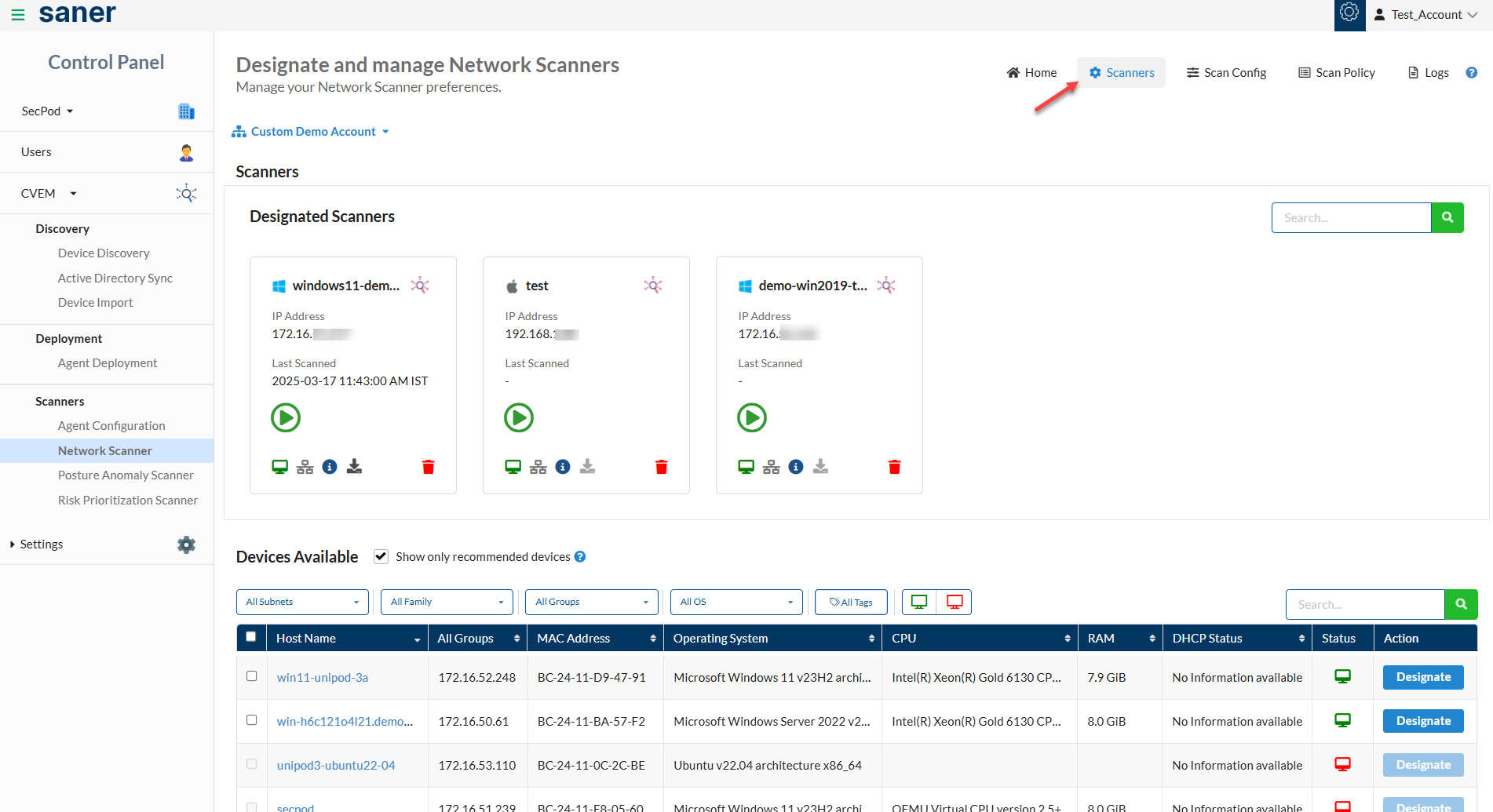
2: Check the box Show only recommended devices to allow Saner’s recommendation engine to choose the best endpoints designated as Network Scanners.
3: Saner shows the endpoints that can be used to designate as Network Scanners. You can do this by clicking the Designate button under the Action column.
The Device Available table displays the below information:
| Field Name | Description |
| Host Name | This column displays the hostname of the endpoint. |
| IP Address | This column displays the ip address of the endpoint. |
| Mac Address | This column displays the mac address of the endpoint. |
| Operating System | This column displays the operating system on the endpoint. |
| CPU | This column displays the processor available on the endpoint. |
| RAM | This column displays the Random Access Memory available on the endpoint. |
| DHCP Status | This column shows if DHCP is enabled on the device. If DHCP is enabled, DHCP Status will be displayed as yes. |
| Status | This column displays the Status of the endpoint. The green system icon indicates that the endpoint is online. And red system icon indicates that the endpoint is offline. |
| Action | This column contains the Designate button. You can use this button to designate an endpoint as a Network Scanner. |
4: Click the Designate button, and the selected endpoint gets designated as a Network Scanner. The Network Scanner is listed under the Designated Scanners section above the Device available table.
The Designated Network Scanner section has multiple icons. The below table describes the usage of each icon.
| Icons | Description |
 | This icon will start the Network Scan when clicked. If this icon is disabled, the device is either shut down or the Saner Agent on the device is inactive. |
 | This icon will abort the ongoing Network Scan. |
 | This icon indicates that the Saner Agent on the designated network scanner is active. |
 | This icon indicates an inactive Saner Agent on the designated network scanner. |
 | This icon indicates that the Network Scanner is active and scanning. |
 | This icon indicates that the last Network Scan was aborted. |
 | This icon indicates that the Network Scanner is idle. |
| This icon provides the details of the last network scan. | |
 | This icon deletes the Network Scanner. |
| This icon downloads the last two network scan reports. However, deleting the designated Network Scanner will delete the reports as well. At the same time, re-designating the Network Scanner will not restore old network scan reports. |
Last Scan Information
Saner Network Scanner stores the results of the network scan performed on the devices on the Saner Server. You can find the last scan details by clicking the ![]() icon.
icon.
The Last Scan Information window displays the following information after every successful network scan:
- Scanner: The name of the scanner used for scanning the network is displayed here.
- Scan Configuration: This label shows the scan configuration used by the network scanner.
- Scan Status: This label shows whether the last scan was successful.
- Scan Summary: This label shows the date, time, the number of hosts scanned, and the total time required to perform the scan.
- Last Scan: This label shows the date and time the previous network scan occurred.
- Next Scan: This label shows the date and time for the next network scan.
- Scan Duration: This label shows the total time required to perform the last network scan.
- Targets scanned: This label shows the count of the total number of devices scanned during the last network scan.
- Targets not scanned: This label shows the total number of devices not scanned during the last network scan.
- Scripts Scanned: This label shows the total number of scripts /policies used during the last network scan.
- Results Uploaded: The status of the Saner Network Scanner uploads the network scan results to the Saner Server.
- Failed to Upload: The Saner Network Scanner could not upload the network scan results to the Saner Server. If the upload fails, it will be shown here.
Manage Scan Configuration
Saner Network Scanner uses a scan configuration to identify targets to scan and exclude the ones not to scan.
Create a new Scan Configuration
1: On the Designate and Manage Network Scanners page, click the Scan Config button.
2: Click the New Scan Config button at the top right side of the page.
A new pop-up appears on the screen. Fill in the information in the text boxes marked with an asterisk (*). Let’s look at each of these textboxes present on the screen and the type of information you need to provide.
Name: – You must specify a name for the Scan Config
Targets – Mention the IP addresses of the targets you wish to scan. The IP addresses must be specified in a comma-separated list of target IP addresses or domain names for scanning. Target IP addresses can also be specified using CIDR notation. For example, 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.1.1/32 or 192.168.1.1-10.
Exclude List: Mention the IP addresses of the targets that need to be excluded by the network scanner while performing a network scan. You can specify multiple IP addresses separated by a comma that needs to be excluded by the Network Scanner.
Scan Type: You can choose between the TCP and TCP&UDP scan you want to perform on the target device. TCP scans require less time than TCP&UDP scans.
Select Ports: This drop-down box provides you with five options. You need to select one of these five options.
- Default Ports
- Top 1000
- Top 500
- Top 100
- None
However, if you want to specify your own set of custom ports, select the checkbox Enter Custom Ports and specify the TCP and UDP ports you want to be scanned by the Network Scanner.
3: Select the Scan Schedule. You can select the scan to run at the below intervals.
- None
- Daily
- Weekly
- Monthly.
4: Click the Create button once you have provided all the information. The Scan Config policy is created and is listed on the Scan Config page.
Edit and Delete a Scan Config
The Action column on the Scan Config page has two options – Edit and Delete.
| Icon | Usage |
| To edit an existing Scan Config. | |
| To delete an existing Scan Config. |
Manage Scan Policy
By default, Network Scanner uses Default Policy to scan devices. Default Policy – a collection of multiple scripts belonging to different families helps Network Scanner to identify vulnerabilities across devices. You can import a new policy, create one, and modify the existing Default Policy.
Create a New Policy
A Default Policy exists in the Saner Network Scanner. The Default Policy consists of preselected scripts. You can modify the scripts you want to be part of the Default Policy. However, you can’t delete the Default Policy; you can change it.
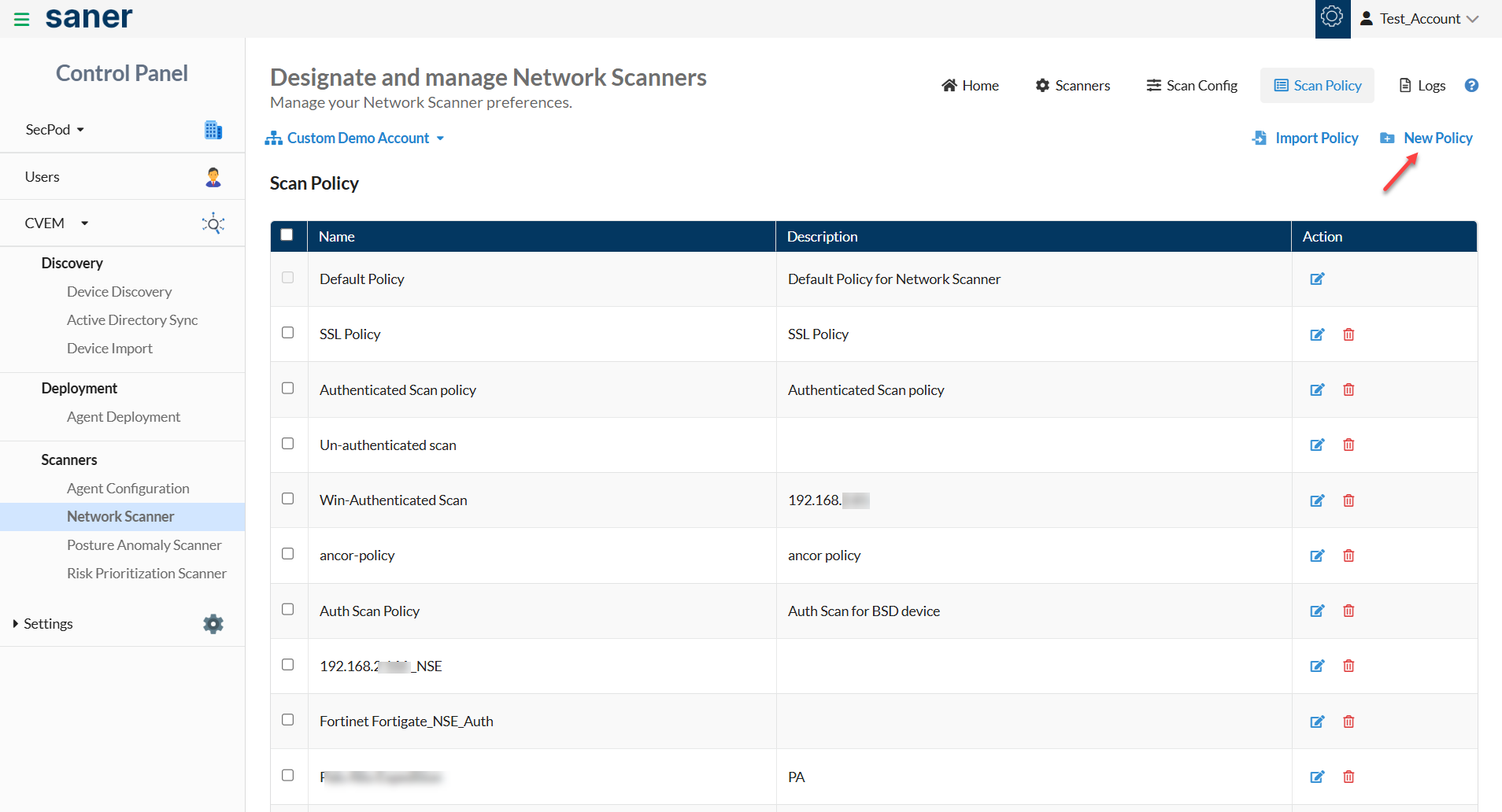
Follow the below steps to create a new policy:
1: Click the New Policy button on the top right of the page.
A new screen appears, prompting you to select the scripts you want to be part of the New Policy.
You can filter the scripts by using the category filter. The scripts fall into the following categories.
- Safe
- Vulnerability
- Exploit
- Default
- Discovery
- Version
- Authentication
Select the scripts category and click the Apply button. A list of scripts relevant to the selected category appears on the page. You can manually deselect scrips you don’t want to be part of the Scan Policy. Click the Next button.
2: Provide the path for the web apps hosted in your environment. The Global Variables input fields will allow you to input the absolute path for these web apps. This step is not mandatory and should be skipped if you have no web apps in your environment. And then provide the set of credentials for the protocol you want the script to authenticate. HTTP/HTTPS and SSH protocols are currently supported. If you’re using HTTP protocol for authentication, you must provide the username and password.
Similarly, if using SSH, you must provide the username, password, private key, and passphrase. Specifying credentials is a mandatory step and cannot be skipped. You can save credentials which will appear on the right side under Saved Credentials section.
3: Specify the Name of the New Policy and provide a brief description in the Description box. Click the Create Policy button, and a new policy is created.
You’ve successfully created a new Scan Policy!
Import Policy
You can import a scan policy from different Accounts within the same Organization. Also, you can import scan policies from Accounts in other Organizations.
Follow the below steps to import a policy from another account:
1: On the Designate and Manage Network Scanners page, click the Scan Policy button.
2: Click the Import Policy button.
2: Select the Organization and the relevant Account from where you want to import the policy. You can only select one policy at a time, even if the Account has multiple policies.
3: Click the Import button. The selected policy gets imported into the current Account and will be visible on the Scan Policy screen.
Perform Authenticated Network Scans
Saner Network Scanner supports authenticated network scanning. New network scripts that support authentication are introduced under the Authenticated category. These scripts allow you to provide credentials and perform an authenticated scan on network devices. Also, the Saner Network Scanner allows you to store credentials that can be used by network scripts that support authentication.
You can create a new policy and add network scripts from the Authenticated category to perform an Authenticated Network Scan. At the same time, you can modify the existing policy to incorporate Authenticated network-scripts to perform an authenticated network scan.
Follow the below steps to create a new policy for performing an Authenticated Network Scan:
1: On the Designate and Manage Network Scanners page, click the Scan Policy button.
2: Click the New Policy button on the top right of the page.
A new screen appears, prompting you to select the scripts you want to be part of the New Policy.
3: Click the filter icon and select the Authentication category. And click the Apply button.
Network scripts from all the existing categories supporting authentication appear on the screen.
4: Select the scripts and click the Next button.
If the network script supports web apps scan, you need to provide the path where the web app resides. Saner Network Scanner will scan the web app using your selected network scripts. If the selected network script supports authentication, you can specify the credentials. Saner Network Scanner supports the following protocols.
- HTTPS/HTTPS
- SSH
For HTTP-type Authentication, you need to provide the following information:
- HTTP Username
- HTTP Password
For SSH-type Authentication, you need to provide the following information:
- SSH Username
- SSH Password OR
a. SSH Private Key
b. SSH Passphrase
Save Credentials in Network Scanner
While creating a new scan policy, your credentials are stored and available only within the created policy. However, Saner Network Scanner allows you to store credentials separately that are not tied to any scan policy and can be used with network scripts that support authentication.
Follow the below steps to save credentials in Network Scanner.
- Click the plus icon next to the Saved Credentials label. Previously saved credentials appear below the Saved Credentials label.
A pop-up window appears on the screen.
Before saving the credentials, select the Authentication Type; you can choose between HTTP and SSH.
If you select HTTP authentication, you need to provide the following information.
Name – Provide the name under which you want the credentials to be saved.
Authentication Type – Select the authentication type as HTTP.
HTTP Username – Provide the username you want the network script to authenticate. HTTP Password – Provide the password for the network script to authenticate.
If you select SSH authentication, you must provide the following information.
Name – Provide the name under which you want the credentials to be saved.
Authentication Type – Select the authentication type as SSH.
SSH Username – Provide the username you want the network script to authenticate.
SSH Password – Provide the password you want the network script to authenticate.
Alternatively, you can provide the Private Key and Passphrase instead of SSH Password.
Perform Agentless Scans on Endpoints
We’ve introduced the Saner Agentless Scanner – a unique scanner that allows you to perform an on-demand scan for vulnerabilities and misconfigurations on your devices without deploying an agent. You can also use the Saner Agentless Scanner to schedule periodic scans.
Saner Agentless Scanner can authenticate to the target devices using SMB and SSH to remote targets. However, the target machines need to meet specific prerequisites.
Pre-requisites needed for performing Agentless Scans
For Linux and Mac Devices
The device should have an SSH Server running on it.
For Windows Devices
- Direct Host (TCP 445) port must be accessible in both Network Scanner and target devices.
- File and Print Sharing must be enabled.
- The %systemroot% share (usually C$ or similar) must be accessible on the target devices.
- A common administrator credential is required to perform authenticated scanning for the targeted Windows devices (both Domain Devices & Local Devices).
For Workgroup Devices
- The LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy must be provisioned to allow a full token on remote login. To do this, you need to make few changes to the registry. Follow the steps below to make the changes to the registry.
- Click Start, click Run, type regedit, and then press Enter.
- Locate and then click the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System - If the LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy registry entry does not exist, follow these steps:
- a. On the Edit menu, point to New, and then click DWORD Value.
- b. Type LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy and then press Enter.
- Right-click LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy and then click OK.
- In the Value data box, type 1, and then click OK.
For Linux and Mac devices
- SSH Server needs to be installed and running (including the Network Scanner if it is a Linux machine).
- The port 22 must be open on all target devices and allowed over the device firewall.
- A common administrator credential (user must have root privileges or should be part of the sudoers list) is required to perform authenticated scanning for the targeted Linux / Mac devices.
| Note: The above requirements apply to target devices where you want to perform Agentless Scans. Endpoints designated as Network Scanners need not meet the prerequisites mentioned above. |
Launch an Agentless Scan on Targeted Devices
You need to ensure that a Network Scanner exists in the Account. Follow the steps in the Designating an Endpoint as a Network Scanner section if a Network Scanner doesn’t exist.
You can create a new Scan Configuration or edit an existing Scan Configuration to specify the target devices’ IP address/ IP address range for the Saner Agentless Scanner to scan. You can refer to the Managing Scan Configuration section to know how to create/edit scan configuration in the Saner Network Scanner.
Create a Scan Policy for Agentless Scanner
1: Click the New Policy button on the top right of the page.
A new screen appears, prompting you to select the scripts you want to be part of the New Policy.
2: Click the filter icon and select the Authentication category. Click the Apply button.
3: Uncheck the Family checkbox. Select the Local Security Check checkbox. You have two scripts under the Local Security Check family – Compliance and Vulnerability Scan. You need an active Saner VM subscription to perform a vulnerability scan. Similarly, you need an active Saner CM subscription to issue a compliance scan on the target devices.
Saner Agentless Scanner allows you to perform an individual scan, such as the Compliance Scan or Vulnerability Scan, or you can perform both scans on the target devices.
4: Select the Authentication type. Saner Agentless Scan supports both SSH and SMB-type authentication on target devices.
For SSH-type Authentication, you need to provide the following information:
- SSH Username
- SSH Password OR
a. SSH Private Key
b. SSH Passphrase
For SMB-type authentication, you need to provide the username and password.
Also, you can use the saved credentials in the Saner Network Scanner to authenticate to target devices. Refer to the Saving Credentials in the Network Scanner section to learn how to save credentials in the Saner Network Scanner.
5: Click the Next button after providing the credentials.
| Note: Saner Agentless Scanner only supports SSH and SMB-type authentication. While saving credentials, ensure you don’t use HTTP-type authentication to authenticate to target devices. |
6: Provide a Name for the newly created policy. You can briefly describe the policy, although it’s not mandatory.
7: Click the Create Policy button to create the Scan Policy.
Assign the Scan Configuration and Scan Policy to the Agentless Scanner
Click the Summary button and assign the Scan Config and Scan Policy to the Agentless Scanner.
Launch the scan by clicking the play ![]() button located right next to the Agentless Scanner. The Agentless Scanner will launch the scan on the target devices specified in the Scan Config.
button located right next to the Agentless Scanner. The Agentless Scanner will launch the scan on the target devices specified in the Scan Config.
View the Agentless Scanner Results
Saner Agentless Scanner stores the scan results performed on the target devices. You can access this information by clicking the ![]() button. You can also download the result in PDF format by clicking the
button. You can also download the result in PDF format by clicking the ![]() button.
button.
The Network Scan Report PDF file has a Vulnerability and Misconfigurations Details section. The target device IP Address is listed in the Impacted Hosts table. Right next to the IP Address, in the bracket, it will be specified as Auth – this indicates the target device was scanned using the Saner Agentless Scanner.
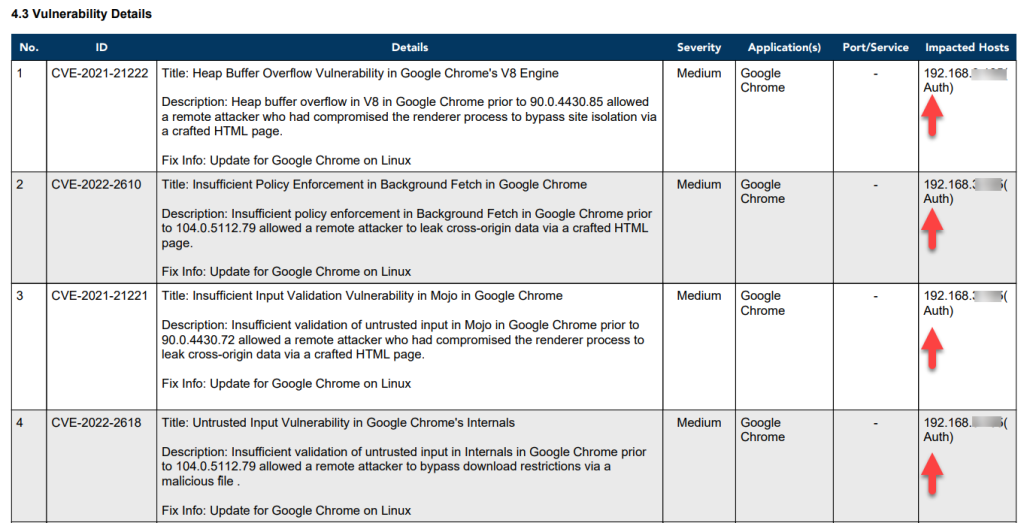
Discover Devices Using Network Scanner
On the Control Panel page, under the Discovery menu, click Device Discovery.
On the Device Discovery page, select the Network Scanner and provide the IP address range. Click the Discover button. Saner Network Scanner will search for devices within the specified range.
You can schedule the Network Scanner to run the discovery scan periodically. The following options are available for scheduling a Device Discovery scan:
- Daily
- Weekly
- Monthly
The devices found by the Saner Network Scanner are listed under the Unmanaged Devices section on the Managed Devices page. This helps you get better clarity on the number of devices that don’t have Saner Agent installed.
You can perform actions on the devices listed under Unmanaged Devices using the Action buttons.
| Button | Usage |
| The Add Device button adds discovered devices into Saner platform. A system administrator can use this button to add multiple devices to Saner platform by importing a CSV file that contains information related to the device. | |
| The Deployment button deploys Saner Agents onto a device. A system administrator can deploy Saner Agent onto a device using the ‘Show Agent Download URL’ or ‘Download Deployer Tool.’ | |
| The Create Group button creates custom groups. You can add devices to these custom groups. | |
| The Delete Device button deletes a device permanently from Saner platform. |
View Network Devices Vulnerabilities
Network Scanner stores the results of the network scan on the Saner server. These results contain the vulnerabilities discovered in devices scanned as part of the network scan by the Network Scanner. You can view all the details associated with the network device (that includes Vulnerabilities, Misconfigurations, Assets, Ports, and Services on the Device Details Page.)
You can access the Device Details page using the below-mentioned pages.
- Managed Device Page.
- Vulnerability Management Dashboard.
- Compliance Management Dashboard.
- Asset Exposure Dashboard.
| Note: Network Scanner only identifies vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in a device. To remediate a vulnerability found in a network device, you must manually remediate it. We recommend using Saner tools to remediate the discovered vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. |
View Network Devices vulnerability on the Device Details Page
On the Menu bar, click the display icon ![]() on the left side of the Admin Dashboard. You will be redirected to the Managed Devices page.
on the left side of the Admin Dashboard. You will be redirected to the Managed Devices page.
On the Managed Devices page, on the right side, you will see all the managed devices available for the selected Account presented in a tabular format.
Here, you can see the devices that Sane Agent and Saner Network Scanner manage.
For devices managed by Network Scanner, under the Managed By column, you can see ![]() icon right next to them. This means that these are network devices and don’t have Saner Agents installed on them. The vulnerabilities discovered in these network devices need manual remediation. We recommend subscribing to Saner tools to help you in remediation.
icon right next to them. This means that these are network devices and don’t have Saner Agents installed on them. The vulnerabilities discovered in these network devices need manual remediation. We recommend subscribing to Saner tools to help you in remediation.
Click the Host Name. This will take you to the Device Details page. You can find all the information related to the device, including CHS Score, Vulnerabilities, Misconfigurations, Assets, Ports, and Services, on this page.
Click here to learn more about the Device Details page.
Device Details Page
You will find all the details related to the network device on the Device Details page. Let’s break down the details displayed on the Device Details Page.
The top section of the page displays the following details:
- Cyber Hygiene Score: The CHS Score for the device will be displayed right below the device icon.
- Device Name: This label displays the host’s name detected during the network scan.
- Operating System: This label displays the name of the operating system detected running on the host during the network scan.
- Mac Address: This label displays the host’s mac address detected during the network scan by the Network Scanner.
- IP Address: This field displays the IP Address assigned to the device.
- Last Scan: This label displays the date and time Network Scanner scanned the device.
- Export Device Report: This button downloads all the details about the host presented on the screen in a .pdf format.
You will find four menu options on the left side of the Device Details page. They’re as
- Device Details
- Posture Anomaly
- Vulnerabilities
- Patches
Assets
This section displays all the software present on the network device with their relevant version number.
Vulnerabilities
This section displays all the vulnerabilities detected in the device.
Misconfigurations
This section displays all the Common Configuration Enumeration (CCE) IDs related to the device.
Ports /Services
This section displays the various ports on the network device, the protocol running on each, and the local address mapped to these ports. Also, this section shows all the services on the device with their current status.
View vulnerable network devices in the Vulnerability Management tool
In the two sections below, you can view vulnerable devices connected to your network in the Saner VM tool.
- Vulnerable Devices Section
- Vulnerabilities Section
Vulnerable Devices Section
On the Saner VM tool dashboard, go to the Vulnerable Devices section. Click the Family filter and select Others to list all the vulnerable network devices in your Account.
Once you apply the Others filter, your screen will look like the screen below.
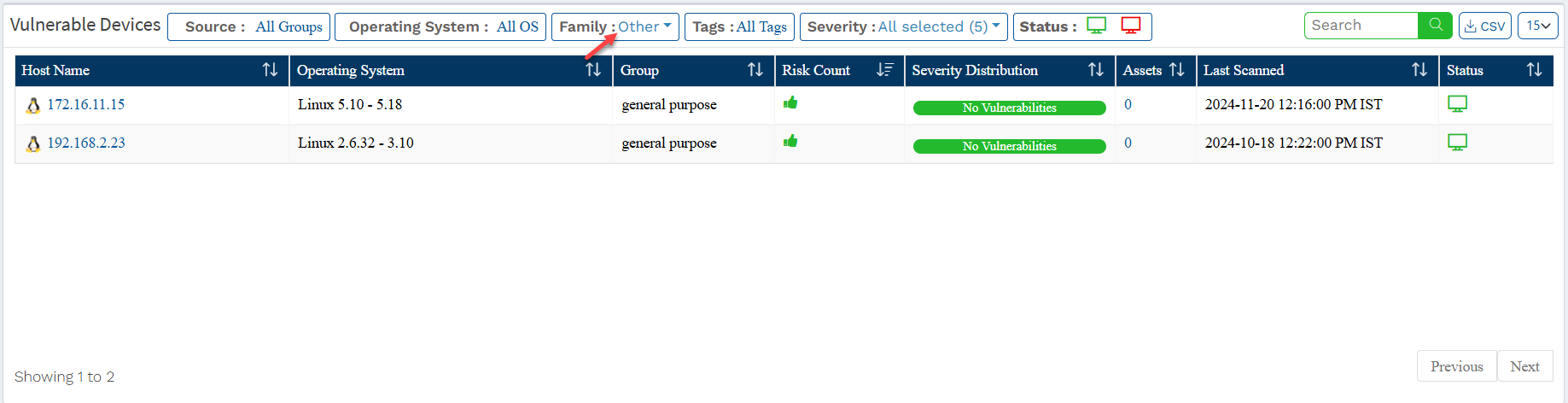
Below mentioned information is presented in the table under the Vulnerable Devices table.
- Host Name: This column displays the hostname of the device. You can click on the hostname, which will take you to the Device Details Page, where you can find detailed information about all the vulnerabilities detected in the device.
- Operating System: This column displays the operating system running on the device.
- Group: This column displays the group to which the device belongs.
- Risks Count: This column displays the total number of vulnerabilities found in the device.
- Severity Distribution: This column displays the breakdown of the total number of vulnerabilities found in the device. The vulnerabilities are categorized into Critical, High, Medium, and Low. And these categories are color coded. They are as follows:
| Vulnerability Category | Color Code |
| Critical | Red |
| High | Orange |
| Medium | Yellow |
| Low | Blue |
6. Assets: This column displays the name and the number of vulnerable software running on the device. You can view the list of vulnerable applications running on the device by clicking the number in the column.
7. Last Scanned: This column displays the date and time a scan was performed on the device.
8. Status: This column displays whether the device is Active or Inactive.
| Note: You will see a thumbs-up icon for devices with no associated vulnerabilities under the Risks Count column and No Vulnerabilities text is shown under the Severity Distribution column. |
Vulnerabilities Section
In the Vulnerabilities section, you can view the vulnerabilities listed by Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) ID. The vulnerabilities table displays Assets, Host, Detected( Released(the day the vendor publicized the vulnerability), . Also, the table shows the date on which the Saner VM tool detected the vulnerability and the relevant fix.
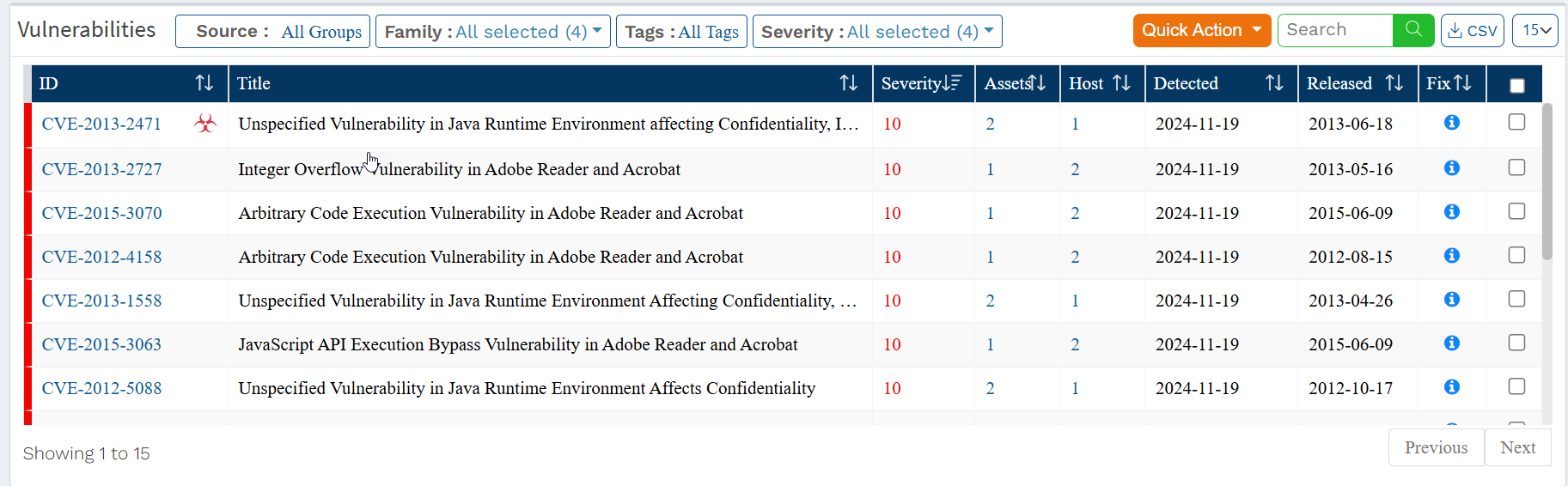
Below mentioned information is presented in the table under the Vulnerable Section:
- ID: This column shows the unique CVE ID associated with the vulnerability detected in the devices.
- Title: This column shows a brief description of the detected CVE.
- Severity: This column shows the Severity score given to the CVE.
- Assets: This column shows the total number of assets the CVE affects in the selected Account.
- Hosts: This column shows the total number of hosts affected by the CVE in the selected Account.
- Detection Date: This column shows the date the vulnerability related to the CVE was detected by the Saner VM tool.
- Release Date: This column shows the date on which the vendor released the CVE related to the vulnerability.
- Fix: This column displays the necessary action to fix the relevant vulnerability.
View Network Scanner Logs
Saner Network Scanner records all the actions performed within the tool and assigns a unique code to each action.
To access the Logs section, click the Logs button on the top right of the Network Scanner page.
Saner Network Scanner logs are displayed in a tabular format. The table below displays the following information:
- Job Code: The Job Code associated with the action performed within the Saner Network Scanner tool.
- Date: The date and time the action was performed within Network Scanner.
- Organization: The Organization to which the Account belongs is displayed here.
- Account: The Account to which the User belongs is displayed here.
- User: The user’s name who performed the action in Network Scanner is displayed here.
- Message: The action performed using the Network Scanner is described here.
You can filter the logs presented in the Log table. The following filters are available:
- Accounts: This filter will display Account-specific logs. You can specify more than one Account at a time while filtering logs by Account.
- Users: This filter displays User-specific logs. You can specify more than one User at a time while filtering logs by User.
- Start Date and Date: This filter can show logs within a specified date range.
To remove any applied filters, click the Clear All button on the top right of the page. If there are multiple log entries, you can limit the log entries displayed on the screen by selecting the value from the Size drop-down box. You can choose 10, 25, 50, and 100 log entries to be shown simultaneously.
The table below lists Saner Network Scanner job codes with their brief description.
| Job Code | Description |
| 14000 | Network Scanner Management |
| 14001 | Initiate Discovery Scan |
| 14002 | Add Discovery Scan Configuration |
| 14003 | Update Discovery Scan Configuration |
| 14004 | Delete Discovery Scan Configuration |
| 14005 | Upload Discovery Scan Data |
| 14006 | Failed to Upload Discovery Scan Data |
| 14007 | Add Network Scan Device |
| 14008 | Failed to Add Network Scan Device |
| 14009 | Updated Network Scan Device |
| 14010 | Failed to Update Network Scan Device |
| 14011 | Failed to Add Discovery Scan Configuration |
| 14012 | Failed to Update Discovery Scan Configuration |
| 14013 | Failed to Delete Discovery Scan Configuration |
| 14014 | Stop Network Scan |
| 14015 | Delete Device |
| 14016 | Failed to Delete Device |
| 14017 | Rename Network Scan Device |
| 14018 | Failed to Rename Network Scan Device |
| 14019 | Updated Device as Network Scanner |
| 14020 | Failed to Update Device as Network Scanner |
| 14021 | Removed Device as Network Scanner |
| 14022 | Failed to Remove Device as Network Scanner |
| 14023 | Initiate Network Scan |
| 14024 | Add Network Scan Configuration |
| 14025 | Failed to Add Network Scan Configuration |
| 14026 | Update Network Scan Configuration |
| 14027 | Failed to Update Network Scan Configuration |
| 14028 | Delete Network Scan Configuration |
| 14029 | Failed to Delete Network Scan Configuration |
| 14030 | Add Network Scan Policy |
| 14031 | Failed to Add Network Scan Policy |
| 14032 | Update Network Scan Policy |
| 14033 | Failed to Update Network Scan Policy |
| 14034 | Delete Network Scan Policy |
| 14035 | Failed to Delete Network Scan Policy |


